Conversational Sequence Diagrams: Visualizing Time-Ordered Interactions and Branching Logic through the AI Chatbot
Sequence Diagrams are the gold standard for showing how objects collaborate to fulfill a specific scenario or use case. They reveal the precise order of messages, the lifelines of participating objects/actors, synchronous vs. asynchronous calls, return values, branching logic (conditions, loops, alternatives), and activation periods—all critical for understanding runtime behavior, identifying potential bottlenecks, race conditions, or missing error handling.
Manually constructing Sequence Diagrams has historically been one of the most tedious modeling tasks:
- Arranging lifelines in the correct order
- Drawing message arrows with proper direction, labels, parameters, and return arrows
- Adding combined fragments (alt, opt, loop, par, ref, neg, critical, etc.)
- Managing activation bars, self-messages, and reply arrows
- Keeping the diagram readable as complexity grows (no overlapping arrows, balanced spacing)
Visual Paradigm’s AI Chatbot eliminates nearly all of this mechanical work. You describe the desired interaction in natural language—exactly as you would explain it to a colleague—and the AI generates a clean, UML 2.5-compliant Sequence Diagram in seconds. Refinements happen through simple follow-up sentences, with Diagram Touch-Up technology preserving layout integrity, rerouting messages intelligently, and maintaining semantic correctness.
How to Create and Refine Sequence Diagrams Conversationally
-
Open the AI Chatbot (chat.visual-paradigm.com or embedded in Visual Paradigm Desktop).
-
Describe the Scenario in Plain English Use clear, narrative-style prompts that specify participants, sequence of actions, conditions, and outcomes. Effective examples:
- “Create a Sequence Diagram for user login with two-factor authentication. Actors: User, Web Browser, Authentication Service, SMS Gateway. Flow: User enters credentials → Browser sends to Auth Service → Auth Service requests OTP from SMS Gateway → SMS Gateway sends OTP → User enters OTP → Auth Service validates → returns success or failure.”
- “Show the checkout sequence in an e-commerce system: Customer, ShoppingCart, OrderService, PaymentGateway, InventoryService. Include happy path, payment failure retry, and out-of-stock abort.”
- “Generate a Sequence Diagram for placing a food delivery order: Customer, Mobile App, Order Service, Restaurant, Payment Processor, Delivery Driver. Show parallel notification to restaurant and payment processing, with a timeout if restaurant doesn’t confirm within 2 minutes.”
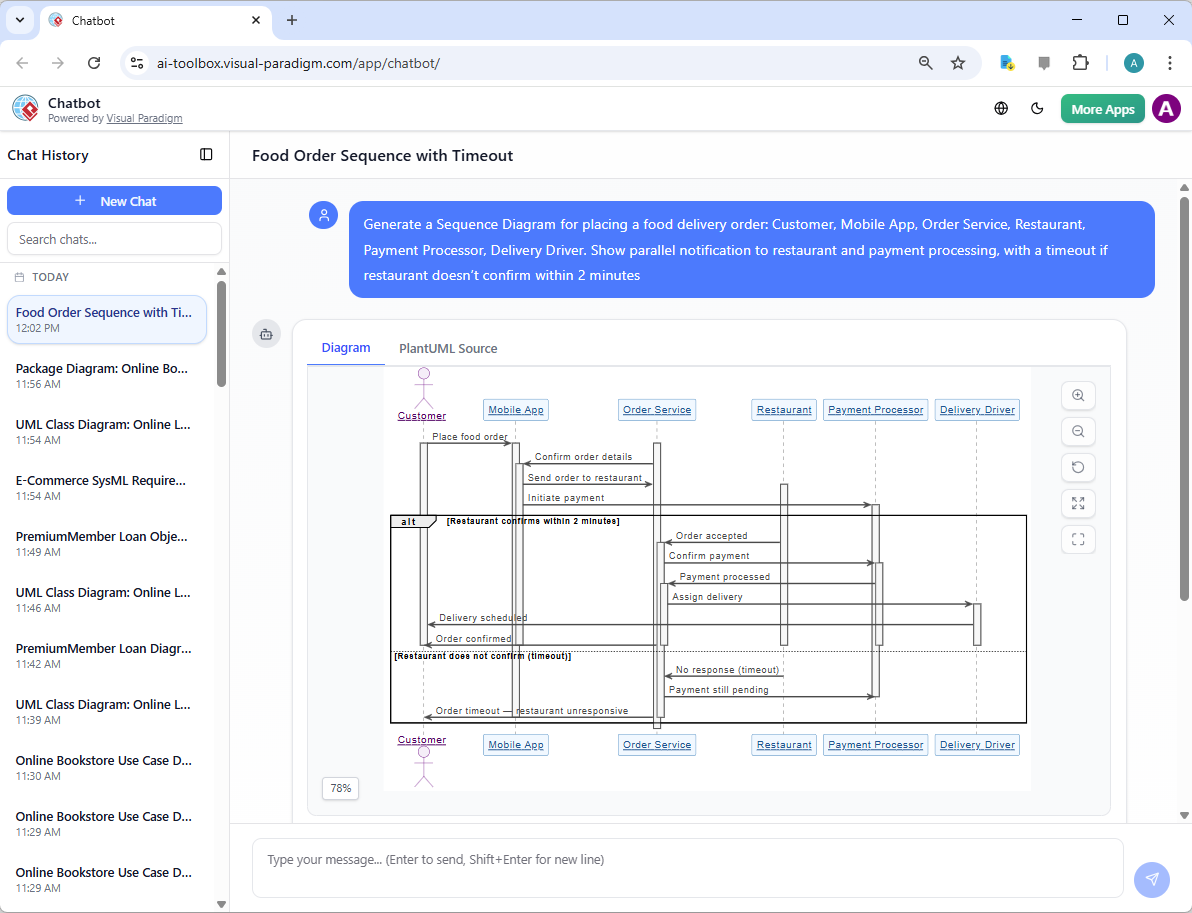
-
AI Generates the Diagram Instantly You receive a fully notated Sequence Diagram featuring:
- Lifelines for each participant (actors as stick figures, objects as rectangles)
- Messages with correct direction (solid arrow for synchronous, dashed for return, half-arrow for async)
- Parameter lists and return values where implied
- Combined fragments:
- alt/else for alternatives (e.g., payment success vs. failure)
- opt for optional steps
- loop for repetitions
- par for parallel execution
- ref for referencing other sequences
- Activation bars showing when objects are processing
- Time progression from top to bottom
- Clean, balanced layout with minimal crossing and readable spacing
-
Refine Iteratively with Natural Language Commands Treat the diagram as a living conversation:
- “Add a retry loop if OTP validation fails (max 3 attempts).”
- “Insert two-factor step only if user has 2FA enabled (use opt fragment).”
- “Show parallel messages: after payment success, notify customer and update inventory simultaneously.”
- “Change the PaymentGateway lifeline to show a timeout after 30 seconds.”
- “Add a self-message on OrderService to calculate total before calling PaymentGateway.”
- “Make the layout horizontal and add a title: ‘Checkout with Payment Retry’.”
- “Highlight the critical section where payment is processed.”
Each command triggers an incremental update—no broken connectors, no lost fragments, no manual repositioning required.
Why Conversational Sequence Diagrams Are Transformative
| Traditional Manual Sequence Diagramming | AI Conversational Approach |
|---|---|
| Hours spent on layout, arrow routing, fragment sizing | Seconds to first diagram, refinements in moments |
| Easy to miss fragments (alt, loop, par) or misuse them | AI infers and applies correct combined fragments from language |
| Hard to maintain readability as complexity grows | Intelligent auto-layout + touch-up preserves clarity |
| Difficult to experiment with alternatives | Safe, instant “what-if” changes via commands |
| Notation errors common (wrong arrow style, missing returns) | Strict UML 2.5 compliance enforced |
| Updates require redrawing large sections | Incremental, semantics-aware edits |
Practical Tips for Powerful Prompts
- Name participants clearly upfront (User, Browser, AuthService, etc.).
- Use words that imply control flow: “if…then…else”, “while”, “after success”, “in parallel”, “retry up to”, “timeout after”.
- Specify architectural layers when relevant: “Show calls from Controller → Service → Repository.”
- Ask for variations: “Show the failure path separately” or “Generate both happy path and exception path in one diagram.”
- Request annotations: “Add notes for preconditions and postconditions.”
Real-World Payoff
- Design Walkthroughs — Generate and project the sequence live during discussions: “This is how login should work—any missing steps?”
- Debugging Early — Spot missing error handling, race conditions, or excessive coupling before coding begins.
- Test Scenario Foundation — Each path through fragments maps directly to test cases.
- Documentation & Onboarding — Clean, self-explanatory diagrams accelerate developer understanding.
With conversational Sequence Diagrams, the most visually and logically demanding UML diagram becomes one of the fastest to create and evolve. The AI handles the notation, layout, and fragment mechanics so you can concentrate on the semantics of collaboration: correct message ordering, appropriate conditions, meaningful branching, and alignment with use-case intent.
This capability sets the stage for even deeper behavioral modeling. In the sections ahead, we’ll explore refining sequences from use cases, layering them architecturally, and modeling object lifecycles with State Machines—all with the same natural, iterative power.

