Automatically Converting User Stories and Text-Based Flows into Actionable Activity Diagrams
Once the high-level Use Case Diagram establishes who does what at a goal-oriented level, the natural next step is to zoom in on how those goals are achieved—detailing the procedural logic, decision points, parallel actions, exceptions, and flows that make the use case executable in practice. Traditionally, this meant manually constructing Activity Diagrams: placing action nodes, drawing control flows, adding decision diamonds, creating swimlanes for actor responsibilities, and painstakingly aligning everything to avoid spaghetti-like layouts.
This manual effort is not only time-consuming but also prone to inconsistencies—especially when multiple use cases share similar flows or when requirements evolve mid-discussion. Visual Paradigm’s AI ecosystem eliminates this bottleneck through Narrative to Activity Diagram Transformation, a powerful capability that turns plain-text descriptions of flows (user stories, main success scenarios, alternative paths, or even meeting notes) into fully structured, standards-compliant Activity Diagrams in seconds.
How the Transformation Works
The process leverages the AI Chatbot (for quick conversational starts) or dedicated Step-Based Apps such as the Use Case to Activity Diagram Converter / Narrative Flow Generator (found in the Innovation Hub or AI Toolbox).
-
Provide the Narrative Start with any textual description of the flow. Common formats that work well include:
- User story style: “As a registered customer, I want to place an order so that I can purchase items from the bookstore. I browse books, add them to my cart, proceed to checkout, enter shipping details, select payment method, confirm order, and receive a confirmation email. If payment fails, I am prompted to try again or choose another method.”
- Numbered main flow + alternatives:
- User selects books and adds to cart
- User proceeds to checkout
- System displays order summary
- User enters shipping address
- User selects payment method (credit card or PayPal)
- System processes payment
- If successful, order is confirmed and email sent Alternative: If payment fails, display error and allow retry or cancel.
- Free-form scenario text from stakeholders or requirements docs.
-
Invoke the Transformation In the AI Chatbot, simply say:
- “Convert this user story into an Activity Diagram: [paste text]”.
Example: Convert this user story into an Activity Diagram: As a registered customer, I want to place an order so that I can purchase items from the bookstore. I browse books, add them to my cart, proceed to checkout, enter shipping details, select payment method, confirm order, and receive a confirmation email. If payment fails, I am prompted to try again or choose another method. - “Generate an Activity Diagram for the ‘Place Order’ use case with main flow and payment failure exception.”
- “Create a swimlane Activity Diagram showing Customer and Payment Gateway responsibilities for checkout.”
Or use a dedicated app: paste the narrative → select diagram type → click Generate.
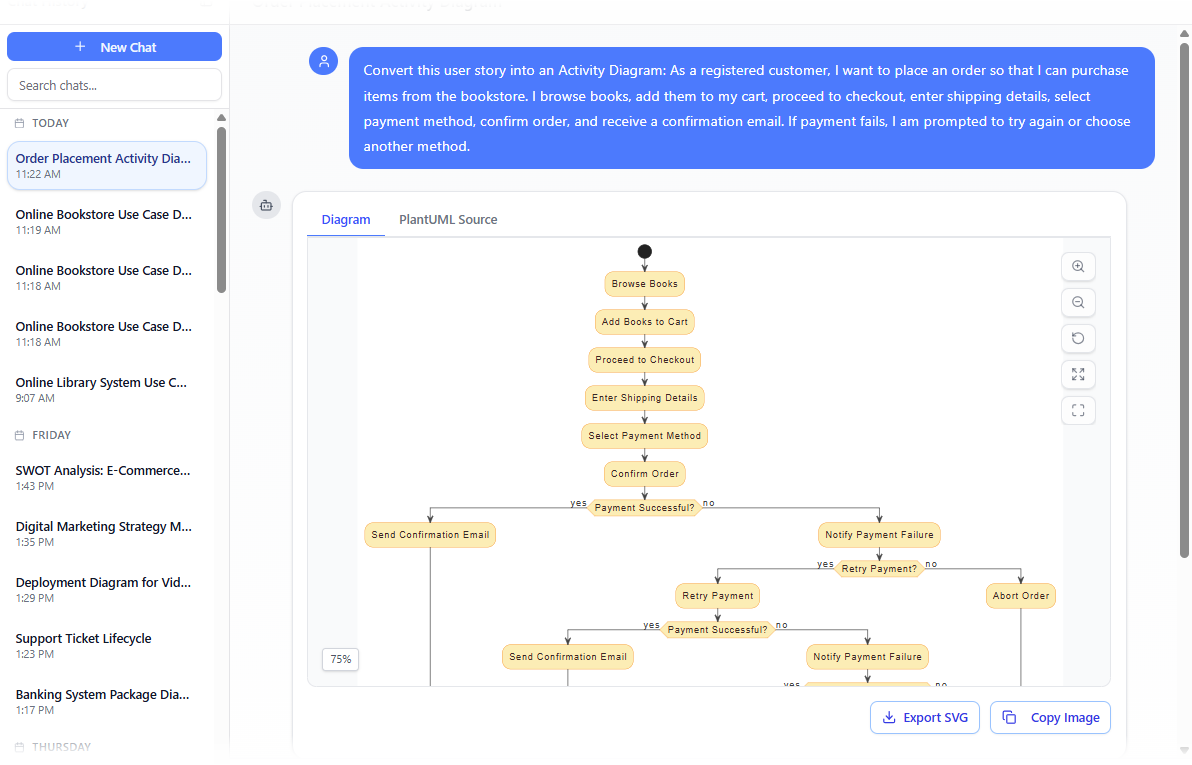
Generate a UML Activity Diagram with Visual Paradigm’s AI Chatbot - “Convert this user story into an Activity Diagram: [paste text]”.
-
Instant Output The AI produces a complete Activity Diagram featuring:
- Initial/Final nodes
- Action nodes (rounded rectangles) with clear, verb-based labels
- Control flows (arrows) showing sequence
- Decision nodes (diamonds) for branches (e.g., “Payment successful?”)
- Merge nodes where paths rejoin
- Fork/Join nodes for parallel actions (if implied, e.g., “send confirmation email” and “update inventory” happen concurrently)
- Swimlanes / Partitions when multiple actors/roles are involved (e.g., Customer | System | Payment Gateway)
- Exception flows routed correctly (often with interruptible regions or labeled guards)
- Clean, auto-arranged layout with minimal crossing lines and readable spacing
-
Iterative Refinement — Treat the diagram as live:
- “Add a step where the system checks inventory before allowing checkout.”
- “Show that ‘Apply Coupon’ is a parallel optional action during checkout.”
- “Include an interruptible region for ‘Cancel Order’ at any point before payment.”
- “Move the Payment Gateway swimlane to the right and color-code customer actions in blue.” Each command triggers a safe, semantics-preserving update via Diagram Touch-Up.
Why This Transformation Is Game-Changing
| Traditional Manual Activity Diagramming | AI-Driven Narrative Transformation |
|---|---|
| Hours spent drawing, aligning, and reconnecting | Seconds to first actionable diagram |
| Easy to miss decisions, parallels, or exceptions | AI infers branches, forks, and error paths from language cues |
| Swimlanes added as afterthought → messy rework | Automatically partitions by actor/system when context provided |
| Hard to keep consistent across related use cases | Reusable style, naming conventions, and layout logic enforced |
| Updates require redrawing large sections | Conversational refinements preserve structure and connections |
Practical Applications & Best Practices
- User Story Mapping to Visual Flow — Convert backlog items into visual workflows for sprint planning or backlog refinement sessions.
- Validation with Stakeholders — Project the generated Activity Diagram during requirements walkthroughs: “Does this accurately show how the checkout should work?”
- Test Case Foundation — Activity paths directly map to acceptance criteria and test scenarios—main flow = happy path, branches = edge cases.
- Early Simulation Insight — Many teams export these early Activity Diagrams to simulation tools to spot bottlenecks or deadlocks before coding begins.
- Prompting Tips — Be explicit about actors (“show swimlanes for Customer and System”), exceptions (“include what happens if…”), and parallelism (“while sending email, also update stock”).
This capability turns what was once one of the most labor-intensive parts of functional modeling into one of the fastest. You describe the desired behavior in natural language; the AI delivers a precise, visual, and editable representation of that behavior—ready for review, refinement, or direct linkage to sequence diagrams in Module 5.
With high-level use cases visualized and detailed flows now automatically rendered, the functional model is taking shape rapidly. The next section shows how to further polish it by intelligently adding and refining «include» and «extend» relationships – ensuring reusability, modularity, and maintainability without manual guesswork.

