State Machine Dynamics: Modeling the Lifecycle of Objects and State Transitions in Response to External Events
While Sequence Diagrams excel at showing interactions between multiple objects over time, they focus on collaboration rather than the internal life of any single object. Many critical domain entities exhibit rich, state-dependent behavior: an Order can be Pending → Paid → Shipped → Delivered → Cancelled; a Booking can be Requested → Confirmed → CheckedIn → Completed → NoShow; a Device can transition from Idle → Active → Error → Recovery. These lifecycles are best captured not in sequences but in State Machine Diagrams (also called Statecharts or State Transition Diagrams in UML 2.5).
State Machines define:
- The possible states an object can be in
- The transitions between states triggered by events
- Guards (conditions) that must be true for a transition to fire
- Effects (actions) executed during or after the transition
- Entry and exit actions for each state
- Do activities (ongoing behavior while in a state)
- Composite states (nested sub-states) and orthogonal regions for concurrent behavior
- History pseudostates for remembering previous sub-states
Manually building State Machines is notoriously complex: states proliferate, transitions multiply, guards become intricate, and layout quickly turns chaotic. Visual Paradigm’s AI ecosystem makes this powerful diagram type accessible and iterative by generating complete, standards-compliant State Machine Diagrams directly from natural-language lifecycle descriptions—then allowing safe, conversational refinement.
How to Model Object Lifecycles with AI
-
Describe the Lifecycle in Plain English In the AI Chatbot (or via dedicated Step-Based Apps like the State Machine Generator), provide a clear narrative of the object’s states and triggers:
- “Model the lifecycle of an Order object: starts in Created state. When payment is received, transitions to Paid. From Paid, can go to Shipped on dispatch confirmation or Cancelled on user request. From Shipped, transitions to Delivered on confirmation or Returned on customer return request. Include a Cancelled state that can be reached from Created, Paid, or Shipped. Add guards, entry actions, and a timeout transition from Created to Cancelled after 24 hours.”
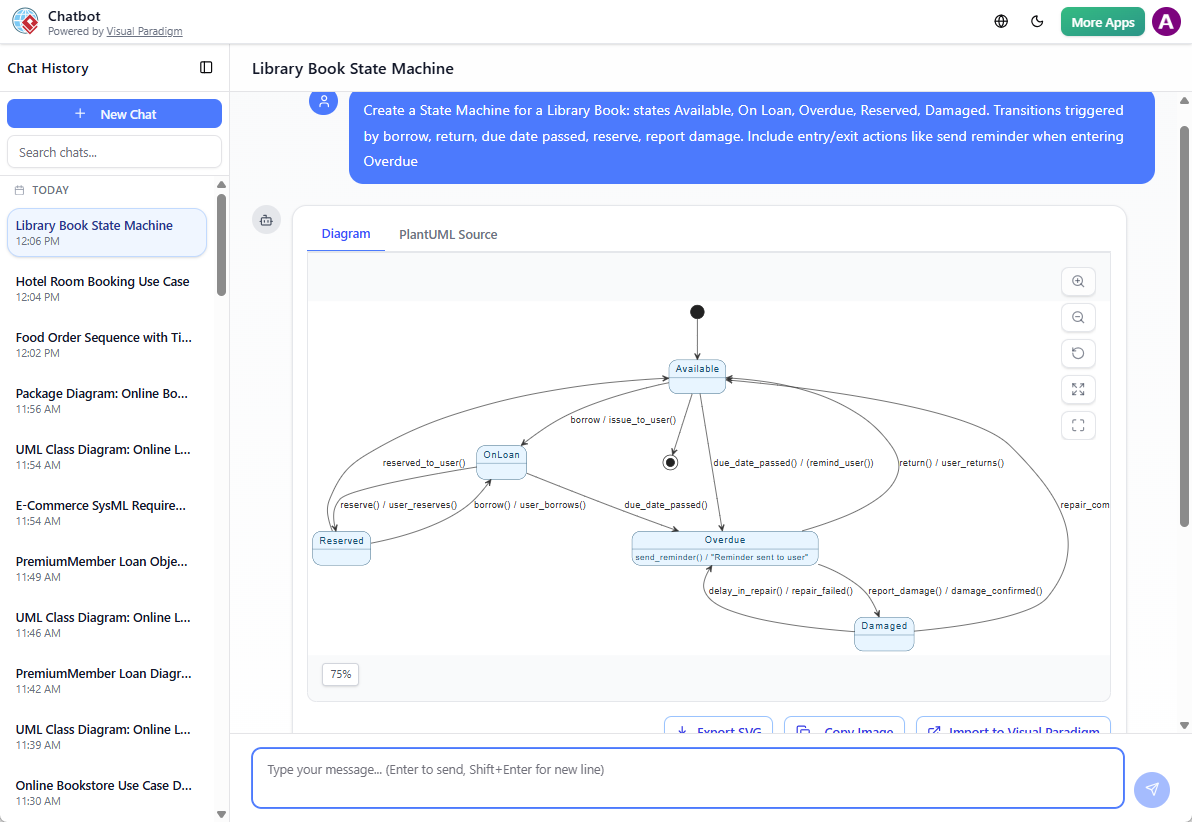
- “Create a State Machine for a Library Book: states Available, On Loan, Overdue, Reserved, Damaged. Transitions triggered by borrow, return, due date passed, reserve, report damage. Include entry/exit actions like send reminder when entering Overdue.”
- “Generate a State Machine Diagram for a Patient Appointment: states Scheduled, Confirmed, CheckedIn, InProgress, Completed, Cancelled, NoShow. Show concurrent regions for payment status (Pending / Paid / Refunded) and show history pseudostate for resuming interrupted sessions.”
-
AI Generates the Full State Machine Diagram The result is a clean, UML 2.5-compliant diagram featuring:
- Rounded rectangles for states (simple and composite)
- Solid arrows for transitions with event[guard]/effect notation
- Black circle for initial pseudostate, bullseye for final
- Diamonds or labels for choice and junction pseudostates
- Entry / Do / Exit actions shown inside states
- Concurrent regions separated by dashed lines
- History (H) or deep history (H*) pseudostates when requested
- Professional layout: hierarchical nesting, minimal crossing, logical flow (left-to-right or top-to-bottom)
-
Iterative Refinement via Natural Language Evolve the model conversationally:
- “Add a Suspended state that can be entered from On Loan on admin hold, and returned to On Loan on release.”
- “Make Cancelled a final state and add a transition from any state to Cancelled on emergency cancellation event.”
- “Insert a timeout transition: from Paid to Cancelled after 7 days if not shipped [guard: !shipped].”
- “Add entry action to Delivered: sendThankYouEmail() and exit action: archiveOrder().”
- “Show orthogonal region for Notification Status: Unsent → Sent → Failed with retry loop.”
- “Change layout to vertical and highlight composite states in blue.”
Diagram Touch-Up technology ensures every change:
- Preserves nesting and region boundaries
- Reroutes transitions intelligently
- Adjusts spacing and alignment
- Maintains semantic correctness (no dangling transitions, valid pseudostate usage)
Why State Machines Are Essential—and Why AI Makes Them Practical
| Challenge in Traditional State Modeling | AI-Generated State Machine Advantage |
|---|---|
| Proliferation of states and transitions | Rapid generation from narrative → fewer missed states |
| Complex guards and effects hard to visualize | Clean notation with event[guard]/effect format |
| Concurrent behavior difficult to draw | Automatic orthogonal regions and concurrent layout |
| Layout chaos in composite or deep hierarchies | Intelligent hierarchical layout + touch-up |
| Hard to iterate when lifecycle rules change | Safe, incremental updates without redrawing |
| Validation against real scenarios is manual | Easy to cross-reference with Sequence/Object Diagrams |
Practical Applications & Best Practices
- Domain-Driven Design — Model aggregates’ lifecycles to enforce invariants (e.g., Order cannot ship if not paid).
- Reactive Systems — Capture real-time or event-driven behavior (IoT devices, workflows, protocols).
- Testing & Simulation — Paths through the state machine become test cases; many tools simulate execution.
- Error & Exception Handling — Explicit transitions to error/recovery states prevent implicit failure modes.
- Prompting Tips:
- Use phrases like “lifecycle of…”, “states: …”, “transitions triggered by…”, “include timeout/guard/entry action”
- Reference domain classes: “For the Order class from my Class Diagram…”
- Request specifics: “show concurrent payment region”, “use shallow history”
State Machines reveal the hidden dynamics within objects—rules that sequences alone cannot fully express. By modeling lifecycles explicitly, you prevent invalid states, catch edge conditions early, and design more robust, predictable systems.
With conversational generation and safe refinement, State Machines move from “advanced” to “essential” in your toolkit. This completes the core behavioral modeling techniques in Module 5: interactions (Sequence), refined collaboration (MVC layering), and internal lifecycles (State Machines). The dynamic view is now comprehensive—ready to support infrastructure, deployment, and advanced architectural frameworks in the modules ahead.

