Exporting AI Models for Code Engineering
Throughout the course, the focus has been on building high-fidelity, standards-compliant models that capture domain knowledge, functional requirements, behavioral dynamics, architectural structure, deployment topology, and enterprise alignment. Now, in the final phase, those models transition from design artifacts into executable implementation assets. This step—often called the “model-to-code” handoff—is where many modeling initiatives historically fail: either the generated code is unusable boilerplate, traceability is lost, or manual coding immediately diverges from the model.
Visual Paradigm eliminates these classic pitfalls through powerful, bidirectional code engineering capabilities that are tightly integrated with its AI-generated diagrams. You can export models directly into production-ready code, while preserving full traceability back to the original UML Class Diagrams. When requirements or architecture change, you update the model and re-synchronize—keeping model and code in harmony throughout the project lifecycle.
How Model-to-Implementation Export Works
-
Prepare the Model for Engineering Ensure your Class Diagram (or set of diagrams) is ready. There are basically three method to prepare a class diagram in Visual Paradigm Desktop:
- Method 1: Draw it manually.
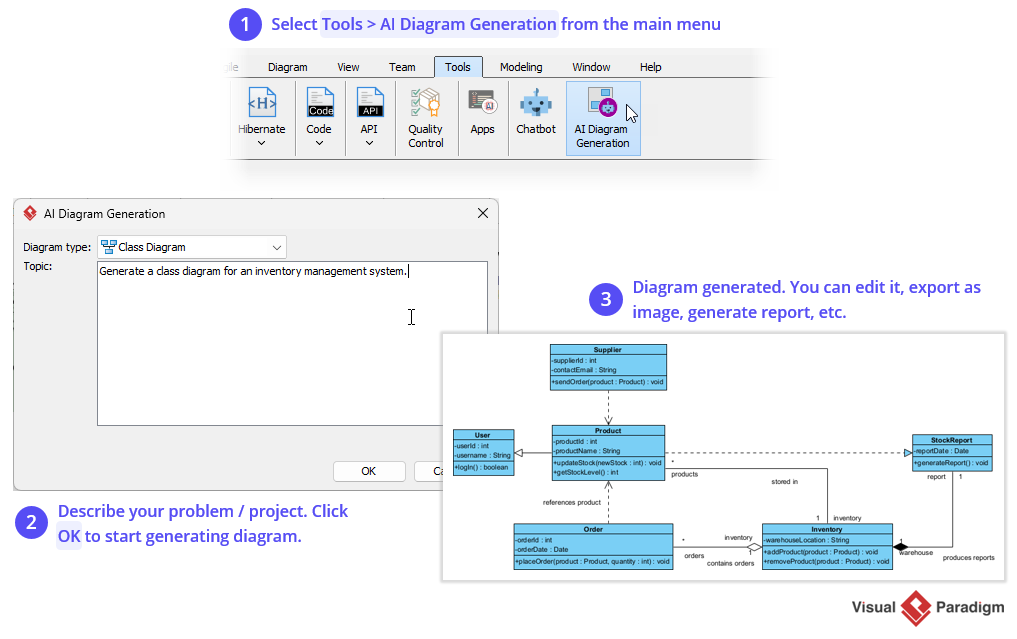
- Method 2: Generate it via the diagram generation tool.
- Method 3: Generate diagram via Chatbot, and then import the resulting diagram into Visual Paradigm.
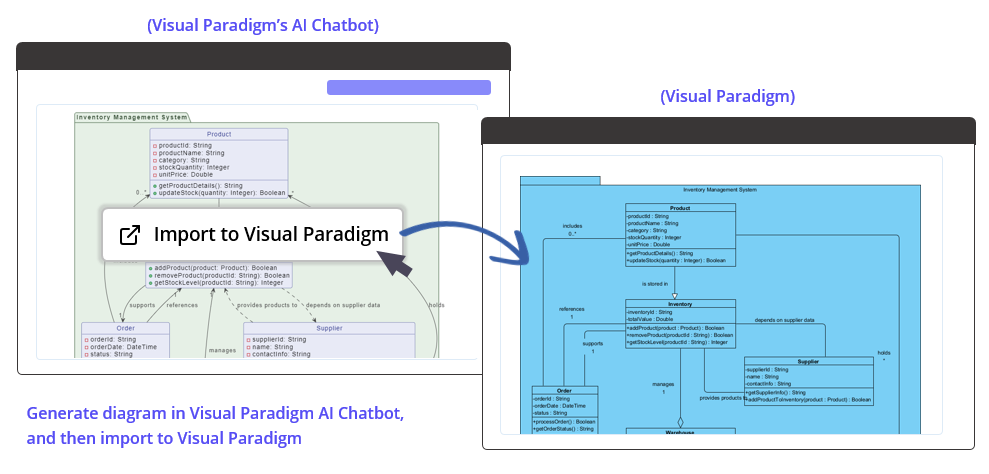
How to import a diagram generated in Visual Paradigm’s AI Chatbot into Visual Paradigm Desktop
-
Choose Your Target Language / Framework Visual Paradigm supports forward engineering to many languages and frameworks, including:
- Java
- C#
- Python
- C++, PHP, VB.NET, and more
-
Generate Code from the Model In Visual Paradigm Desktop (Standard / Professional / Enterprise Edition):
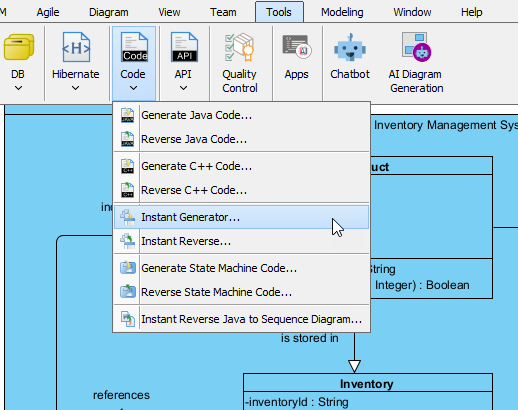
- Select Tools > Code > Instant Generator….
- Select the language/framework.
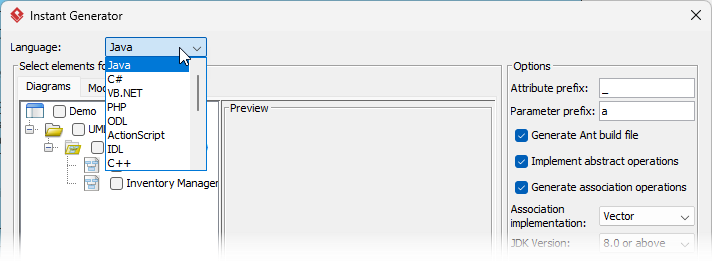
- Click Generate → full source files appear in your project folder
- Select Tools > Code > Instant Generator….
-
Round-Trip Synchronization (Keeping Model & Code Aligned)
- Forward engineering: Model → Code (update classes, add methods)
- Reverse engineering: Code → Model (import existing codebase to create/update diagrams)
- Sync on demand: Compare model vs. code → show differences → merge changes in either direction
- Ideal for agile teams: refactor in model → regenerate code stubs → implement details → reverse changes back
Why This Engineering Flow Succeeds Where Others Fail
| Common Model-to-Code Pitfalls | Visual Paradigm + AI Advantages |
|---|---|
| Generated code is rigid boilerplate | Configurable templates + framework-aware patterns (Spring, JPA) |
| Traceability lost after first code edit | Bidirectional round-trip keeps model/code in sync |
Practical Tips & Best Practices
- Start with domain classes first → generate entities + mappings
- Use stereotypes/tags for hints: <<entity>>, <<repository>>, <<service>>, <<embeddable>>
- Commit generated code to version control → treat it as first-class source
Real-World Impact
- Accelerated Development — Teams start with correct domain model + ORM mappings + basic CRUD → focus on business logic
- Reduced Technical Debt — Model/code sync prevents drift
- Better Onboarding — New developers see visual model + generated code aligned
- Audit & Compliance — Traceable path from requirements → model → code
This export-to-implementation capability closes the gap between design and delivery. The AI-generated models are no longer “nice to have”—they become the authoritative source for code structure, dramatically shortening the path from architecture to working software.

