What are the five stages of project management?
The project management process is usually broken down into phases according to its life cycle, starting from Project Initiation and ending in Project Closure. Each phase has its own goals, activities, and deliverables, making it easier to control the project and the quality of output in general.

According to the PMBOK Guide (Project Management Body of Knowledge) by the Project Management Institute (PMI), a project management life cycle has 5 distinct phases:
- Project Initiation
- Project Planning
- Project Execution
- Project Monitoring
- Project Closure
In this project management guide, we will take a closer look at these five phases.
Phase 1: Project Initiation
The project initiation phase is the first phase of a project life cycle. It’s where abstract ideas are converted into meaningful project goals.

During the project initiation phase, you need to develop a business case and define the project, which involves defining the project’s requirements and creating a project charter.
What is a project charter? Well, the project charter documents the project constraints, objectives, budget, project timeline (high level), etc. Note that the project charter does not contain any technical details, which will be collected and documented during the project planning phase.
Once the project goals are scope are identified, identify the stakeholders involved in the project. A stakeholder is someone who has an interest in the project, and he/she/they can influence the project (e.g., the project development process) or the outcome of the project (e.g., the system to be developed), or be affected by the project. Typical stakeholders are sponsors, customers, board members, developers, suppliers, or partners. Document the role of the stakeholder, the type of interest/influence, and the communication requirements.
Phase 2: Project Planning
The project planning phase consists of an in-depth overview of the project’s goals and requirements. Typically, it accounts for almost half of the entire project time span.
During the planning phase, the project deliverables and requirements are defined and the project schedule is created.
It involves creating a set of plans to help manage time, cost, quality, change, risk, and related issues. They will also help you control staff and outside vendors to ensure you deliver the project on time and within budget and schedule.
Here are the basic processes of project planning:
- Scope planning – Define the boundary of the project by specifying the scope of the project, which is essential to facilitate creating the work breakdown structure.
- Work breakdown structure – Break down a project into tasks and sub-tasks to make it more manageable.
- Project schedule – Scheduling of activities and detailing their dependencies
- Resource planning – identify who will do what work, at which time and if any special skills are needed to accomplish the project tasks
- Budget planning – specify the budgeted cost to be incurred at the completion of the project
- Procurement planning – focus on vendors outside your company and subcontracting
- Risk management – identify the possible risks and work out optional contingency plans and/or mitigation strategies
- Quality planning – assessing quality criteria to be used for the project
- Communication planning – designing the communication strategy with all project stakeholders
Phase 3: Project Execution
The project execution phase is where the project team does the actual work to turn the project goals into deliverables.

It is important for the project to maintain an effective collaboration between project stakeholders and ensure that everyone stays on the same page.
Phase 4: Project Monitoring and Controlling
The monitoring and controlling of a project run simultaneously with project execution to ensure the objectives and deliverables are met.
In this phase, the project manager has to ensure the original plan is properly implemented by establishing the Critical Success Factors (CSF) and Key Performance Indicator (KPI).
So what are Critical Success Factors? What are Key Performance Indicators?
Critical Success Factors are the conditions, capabilities, events, and circumstances that contribute to project success. The purpose of identifying the critical success factors is to ensure that the project success criteria defined can be met.
A key performance indicator (KPI) is a measurable value that demonstrates how effectively the team is achieving the project goals defined. Project teams use KPIs to evaluate success at reaching targets.
Phase 5: Project Closing
As the final phase of the project management process, the Project Closing refers to the activities to perform after the final delivery of the project, which typically includes a discussion of lessons learned throughout the project, the termination of contracts, etc.

Lessons Learned document the lessons learned based on both the positive experiences and the negative experiences that result in undesirable outcomes. Lessons learning is a process to convert experiences into knowledge to aid future decision-making and problem-solving. It helps improve project performance, avoid mistakes from happening again, and maintain good practices.
Finally, a detailed report is written that covers the different aspects of the project. The report, along with other necessary data is stored somewhere for future access.
Any project management software that helps?
Sure! Visual Paradigm is a leading project management software, used by government, corporate, and agencies, enabling millions of project teams to plan and conduct projects and collaborate more effectively.
Visual Paradigm features several project management tools. Let’s go through some of them below.
- Just-in-Time PMBOK Process Map: A matrix of PMBOK processes. Each process involves a set of steps, and each step consists of action item(s) you need to perform to get the activity done.
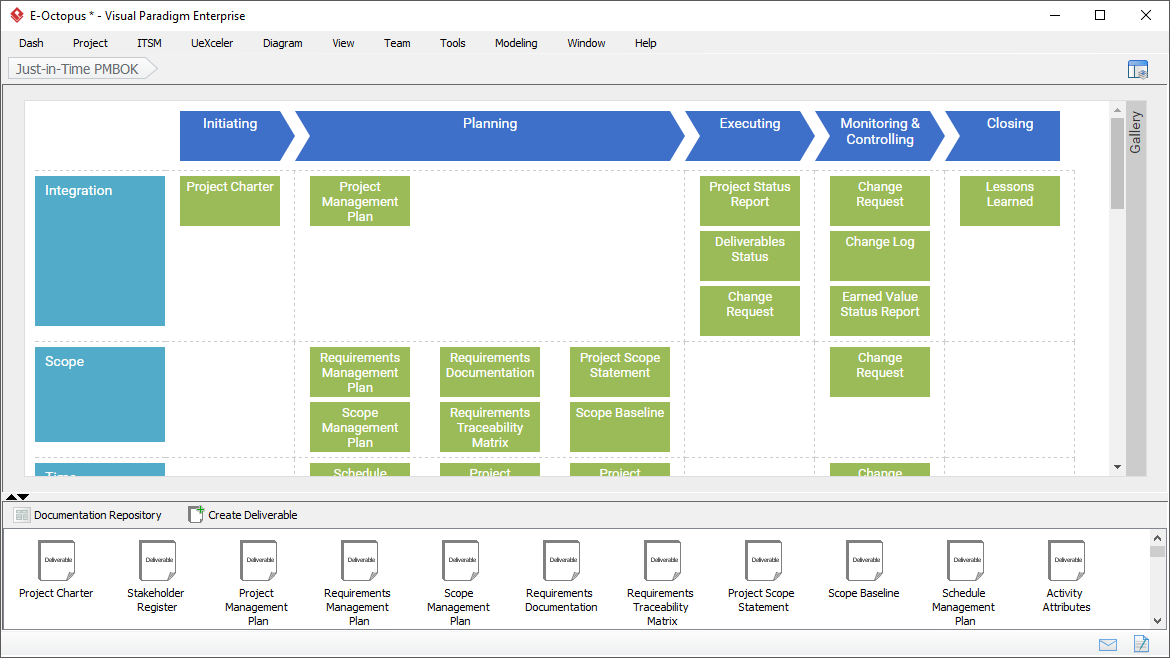
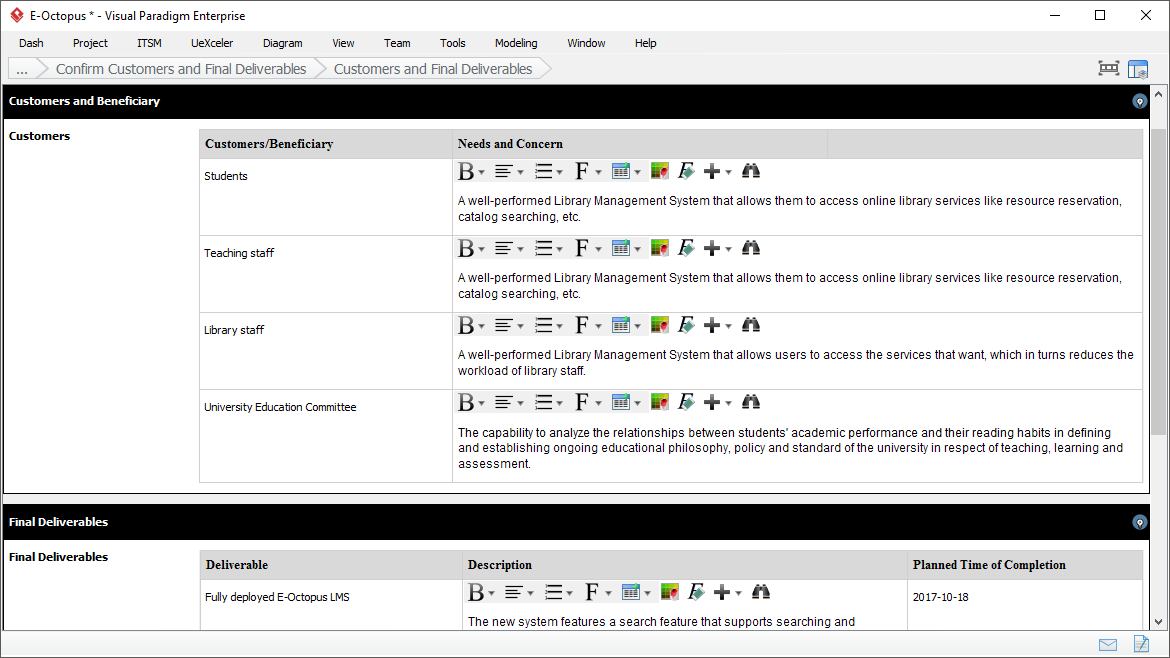
- Project management tool that guides you through the activities of a project life cycle. Each activity requires you to perform certain actions, which include but are not limited to form filling (e.g. create a Project Charter) and diagram creation (e.g. create a PERT Chart). The information entered is consolidated to form the project documents/deliverables.
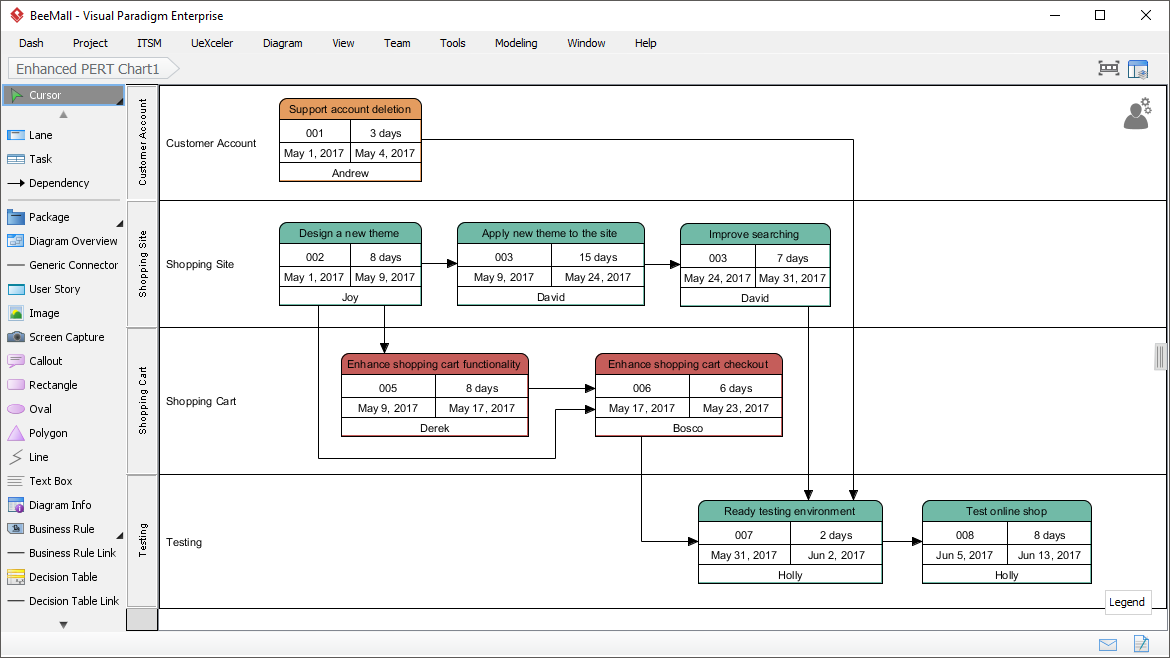
- Diagram tools for project management: A rich set of project management diagram tools are supported to assists you in the creation of project charter, project plans, and more. This includes PERT Chart, Work Breakdown Structure, Fishbone Diagram, Org. Chart, Roadmap & Implementation Plan, GANTT Chart, Radar Chart, etc.
What else can I do with Visual Paradigm?
Visual Paradigm is a full-featured modeling platform that supports a rich set of standards and notations. Here is a shortlist of things you can do with Visual Paradigm:
- Create UML diagrams
- Access to the full set of standard UML notations
- Ensure the correctness of modeling syntax with syntax checking on-the-fly
- Easy-to-use drag-and-drop UML editing tool
- Quick diagram creation with the Resource-Centric interface
- Precise positioning of shapes with alignment guide
- Inline shape editing
- Alignment and distribute functions
- Rich set of formatting options
- Maintain model elements
- Group models and diagrams by packages/model shapes
- Model traceability
- Team collaboration
- Work with the team concurrently and collaboratively with team collaborative features
- Keep revisions for your ER diagrams
- Smart conflict resolution for conflicting changes
- Publishing / Sharing
- Publish and share ER diagrams online
- Export diagrams as image files
- Document creation
- Coverage of additional model types
- Scrum and Agile
- Project Management
- User / Customer Experience
- TOGAF support
- Visual TOGAF ADM process map with actionable work items
- Produce deliverables as you progress through the enterprise architecture development cycle
- Additional Enterprise Architecture toolset
- DoDAF process map
- NAF process map
- MODAF process map
How do I download Visual Paradigm?
Visual Paradigm comes with 30 days trial period. You can visit our download page to download Visual Paradigm.














