What is a Capability Map in EA?
A Capability Map in the context of Enterprise Architecture (EA) is a strategic tool that visually represents the capabilities of an organization. It outlines the relationship between various business functions and processes, providing an overview of what the organization can do to achieve its objectives. The map serves as a foundation for aligning business capabilities with strategic goals, facilitating informed decision-making.
Why Use a Capability Map in EA Development?
- Strategic Alignment: Ensures that business capabilities are aligned with the organization’s strategic objectives, helping to prioritize initiatives.
- Gap Identification: Aids in identifying capabilities that are lacking or underperforming, which can hinder the organization’s ability to meet its goals.
- Improved Communication: Serves as a visual communication tool for stakeholders, simplifying complex information about capabilities and their interrelationships.
- Resource Optimization: Helps in understanding resource allocation and identifying areas where additional investment might be needed.
- Facilitation of Change: Supports change management efforts by providing a clear view of how capabilities can evolve in response to market demands or internal shifts.
How to Create a Capability Map for EA Development
Step 1: Define the Purpose and Scope
- Clarify Objectives: Determine what you want to achieve with the capability map. Common objectives include assessing current capabilities, planning for future development, or identifying areas for improvement.
- Involve Stakeholders: Engage key stakeholders from different departments to gather insights and ensure their needs are represented.
Step 2: Gather Data on Capabilities
- Identify Existing Capabilities: Compile a list of capabilities across the organization, as shown in the example with categories like Product Management, Marketing, Sales and Distribution, and Customer Care.
- Conduct Interviews and Workshops: Gather qualitative data from team members to understand how each capability operates and its significance.
Step 3: Categorize and Prioritize Capabilities
- Group by Function: Organize capabilities into relevant categories (e.g., Business Management, Asset Management, Business Support) based on the organizational structure.
- Prioritize: Determine which capabilities are critical to achieving strategic objectives and which may require enhancement or development.
Step 4: Create the Capability Map
- Select a Modeling Tool: Use ArchiMate-compatible tools (like Archi, Sparx Enterprise Architect, or others) to create the capability map.
- Visual Representation: Represent each capability as a box in the diagram. Use connecting lines to show relationships and interdependencies between capabilities.
Step 5: Analyze the Capability Map
- Evaluate Performance: Assess each capability’s effectiveness and how well it aligns with strategic goals.
- Identify Gaps and Risks: Look for capabilities that are underperforming or missing, which could pose a risk to achieving strategic objectives.
- Assess Interdependencies: Understand how capabilities interact and support one another, identifying potential areas for integration or improvement.
Step 6: Develop Recommendations
- Strategic Initiatives: Propose initiatives to strengthen capabilities, fill gaps, or realign resources. For example, if customer service capabilities are lacking, recommend investing in training or new technologies.
- Implementation Roadmap: Create a clear action plan outlining steps, timelines, and responsible parties for enhancing identified capabilities.
Step 7: Communicate Findings
- Present the Capability Map: Share the map with stakeholders to provide a visual overview of organizational capabilities and their strategic importance.
- Documentation: Prepare a comprehensive report summarizing the analysis, findings, and actionable recommendations.
Step 8: Continuous Monitoring and Updating
- Establish KPIs: Define key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure the effectiveness of capabilities over time.
- Regular Revisions: Schedule periodic reviews of the capability map to ensure it remains relevant and reflects changes in the organizational strategy or market conditions.
Case Study: Utilizing an ArchiMate Capability Map for Strategic Alignment
This case study examines an organization’s capability map, illustrated in the provided ArchiMate model. The map categorizes various business functions and capabilities, demonstrating how they align with the organization’s strategic objectives. By analyzing this capability map, we can gain insights into the organization’s strengths, weaknesses, and opportunities for improvement.
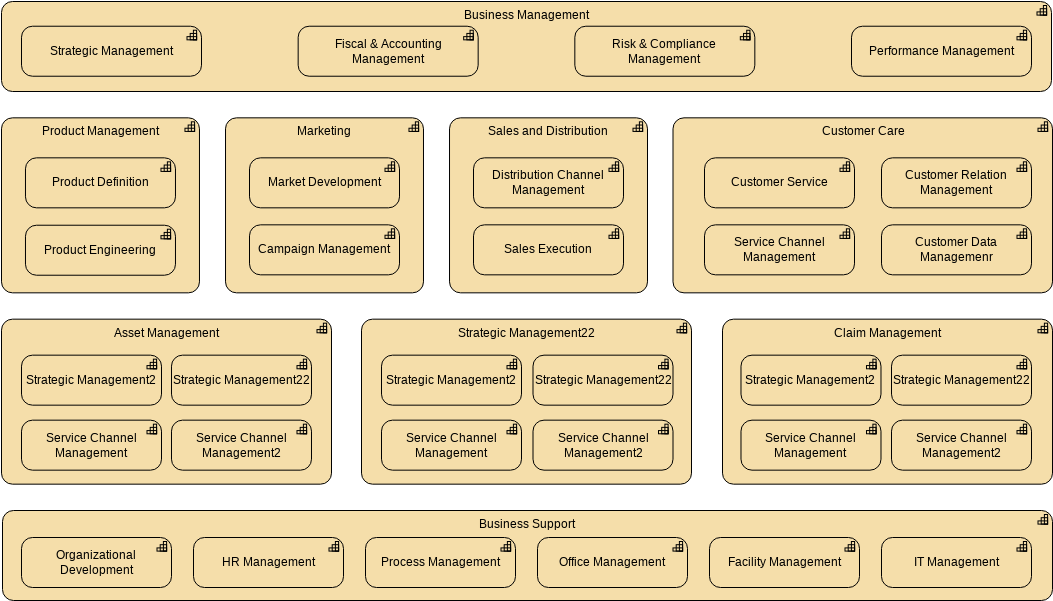
Capability Map Overview
The capability map consists of the following main categories:
- Business Management
- Product Management
- Product Definition
- Product Development
- Product Engineering
- Marketing
- Market Development
- Campaign Management
- Sales and Distribution
- Distribution Channel Management
- Customer Service
- Customer Care
- Customer Service Management
- Customer Relationship Management
- Customer Data Management
- Product Management
- Asset Management
- Strategic Management
- Strategic Management 1
- Strategic Management 2
- Claim Management
- Claim Processing
- Claim Analysis
- Strategic Management
- Business Support
- HR Management
- Process Management
- Office Management
- Facility Management
- IT Management
Objectives of the Capability Map
The primary objectives of the capability map are:
- Align Capabilities with Strategic Goals: Ensure that all capabilities support the organization’s mission and vision.
- Identify Gaps and Opportunities: Determine areas where capabilities may be lacking or underperforming.
- Enhance Communication: Provide a clear visual representation that facilitates discussions among stakeholders.
Analysis of the Capability Map
Strengths
- Comprehensive Coverage: The map covers essential areas of the business, including management, asset handling, and support functions, indicating a well-rounded approach to capability development.
- Clear Structure: The categorization of capabilities into distinct areas facilitates understanding and allows for targeted analysis.
Weaknesses
- Overlapping Capabilities: Some capabilities, such as those in Product Management and Marketing, may have overlapping functions, suggesting a potential need for clarification and integration.
- Underdeveloped Areas: Certain areas, such as Claim Management, may require further development to meet strategic objectives effectively.
Opportunities for Improvement
- Enhance Customer Care: Investing in capabilities related to customer service and relationship management can lead to improved customer satisfaction and retention.
- Optimize Asset Management: Strengthening strategic management capabilities could enhance decision-making and resource allocation.
Recommendations
- Conduct Workshops: Engage relevant stakeholders in workshops to clarify overlapping capabilities and streamline processes.
- Invest in Training: Focus on training programs for staff involved in customer care and claim management to enhance their effectiveness.
- Regular Reviews: Establish a routine for reviewing the capability map to ensure it remains aligned with evolving strategic goals and market conditions.
Conclusion
A Capability Map is a vital tool in Enterprise Architecture development, providing a structured view of an organization’s capabilities and their alignment with strategic objectives. By following this tutorial, you can effectively create and utilize a capability map to enhance decision-making, identify gaps, and optimize resource allocation. This approach not only clarifies what the organization can achieve but also supports ongoing efforts to adapt and thrive in a dynamic business environment.














