Introduction to Enterprise Architecture (EA)
Enterprise Architecture (EA) is a strategic framework that defines the structure and operation of an organization. It provides a blueprint for aligning business strategy with technology, ensuring that the organization’s IT infrastructure supports its goals and objectives. By establishing a clear framework, EA facilitates better decision-making, improved communication, and enhanced agility in responding to changes in the business environment.
Key Goals of EA
- Alignment: Ensure that IT investments align with business objectives.
- Standardization: Promote consistency and reduce redundancy across the organization.
- Agility: Enable quick adaptation to changing business needs and technology trends.
- Governance: Establish frameworks for compliance, risk management, and performance measurement.
Overview of TOGAF
The Open Group Architecture Framework (TOGAF) is one of the most widely used EA frameworks. It provides a structured approach for designing, planning, implementing, and governing enterprise architectures.
Components of TOGAF
TOGAF consists of several key components:
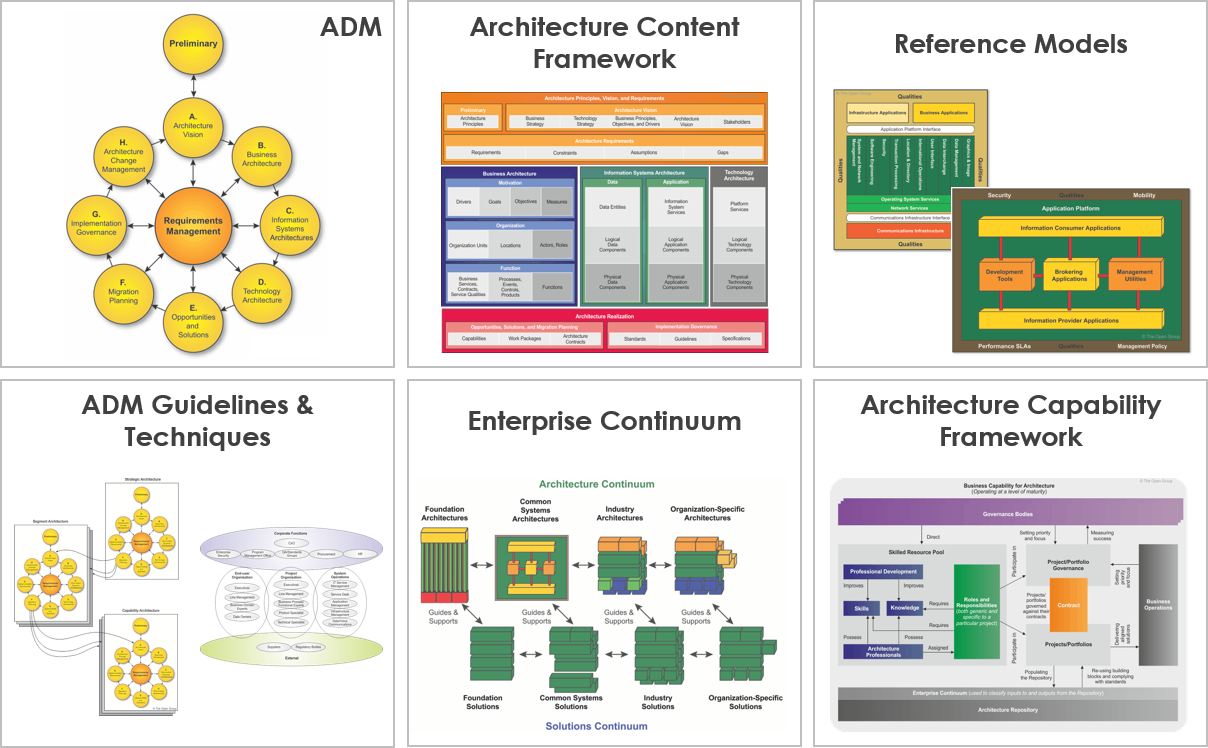
- Architecture Development Method (ADM): A step-by-step approach for developing and managing the architecture.
- Architecture Content Framework: Outlines the deliverables and artifacts produced during the architecture development process.
- Enterprise Continuum: A model for categorizing architecture and solutions from generic to specific.
- Architecture Capability Framework: Provides guidelines for establishing and maintaining an architecture practice within the organization.
Phases of ADM
TOGAF’s ADM consists of several phases:
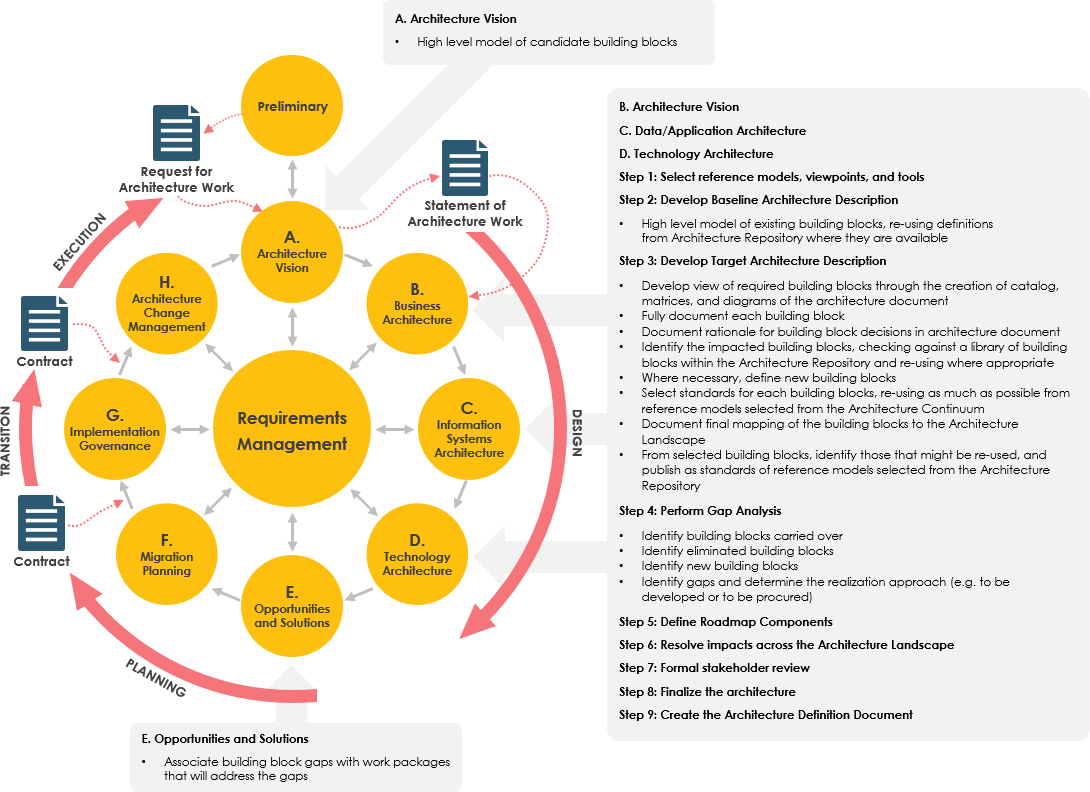
- Preliminary Phase: Prepare and customize the architecture framework.
- Phase A: Architecture Vision: Define the scope, objectives, and stakeholders.
- Phase B: Business Architecture: Develop a view of the business strategy, governance, organization, and key business processes.
- Phase C: Information Systems Architectures: Create architectures for data and applications.
- Phase D: Technology Architecture: Define the technology infrastructure required to support the architecture.
- Phase E: Opportunities and Solutions: Identify and plan for implementation projects.
- Phase F: Migration Planning: Develop a roadmap for implementing the architecture.
- Phase G: Implementation Governance: Ensure compliance with the architecture during implementation.
- Phase H: Architecture Change Management: Manage changes to the architecture over time.
Different Types of EA Frameworks
There are several EA frameworks in addition to TOGAF, each with unique features and benefits. Here are a few notable ones:
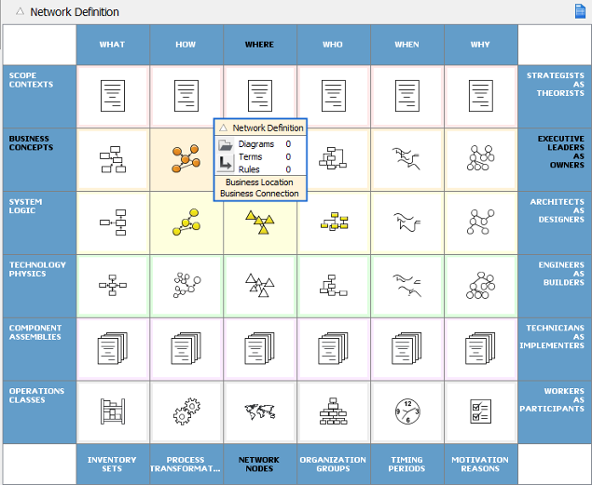
1. Zachman Framework
The Zachman Framework is a schema for organizing architectural artifacts. It provides a structured way to view and analyze an organization’s architecture from different perspectives (e.g., planner, owner, designer) and focuses on the “who,” “what,” “where,” “when,” “why,” and “how” of the architecture.
2. FEAF (Federal Enterprise Architecture Framework)
The Federal Enterprise Architecture Framework is used by U.S. federal agencies to facilitate cross-agency collaboration and improve the efficiency of government operations. FEAF focuses on aligning IT investments with business outcomes and includes various reference models.
3. Gartner EA Framework
The Gartner EA Framework emphasizes the importance of business outcomes and strategic alignment. It provides a flexible approach that allows organizations to tailor their EA practices based on their specific needs and contexts.
4. DoDAF (Department of Defense Architecture Framework)
DoDAF is designed for use within the U.S. Department of Defense and its contractors. It focuses on providing a comprehensive view of the architecture, ensuring that all aspects of defense operations are considered.
Conclusion
Enterprise Architecture is a vital discipline that helps organizations align their IT strategies with business objectives. TOGAF, as one of the leading frameworks, provides a structured methodology for developing and managing these architectures. Understanding various EA frameworks, including TOGAF, Zachman, FEAF, Gartner, and DoDAF, allows organizations to choose the right approach that fits their unique needs and promotes effective decision-making and strategic alignment. By leveraging these frameworks, organizations can enhance their agility, governance, and overall performance in an increasingly complex business environment.














