Visualizing the time ordering of messages between participants in an interaction
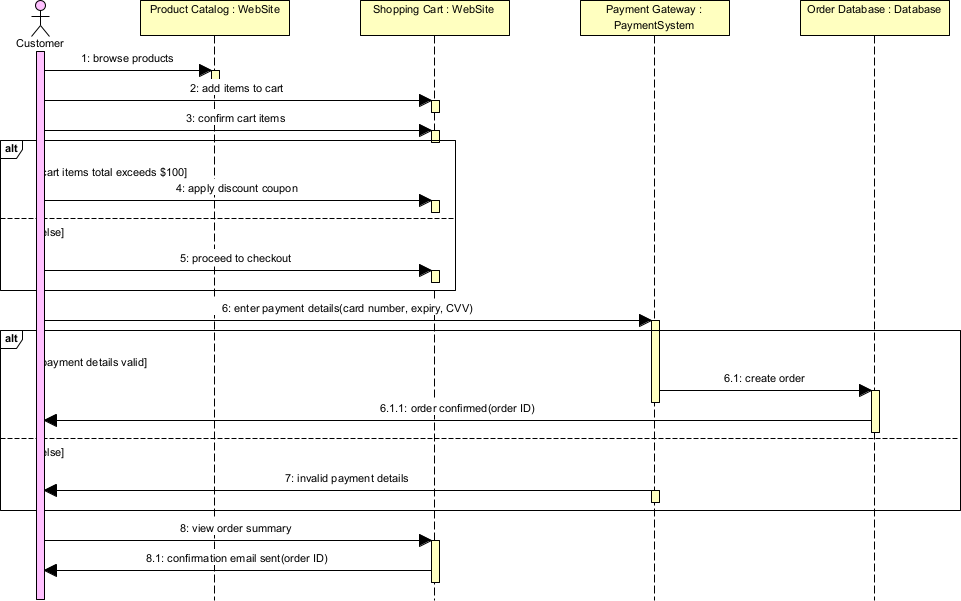
Shipping cart checkout sequence diagram example
Sequence diagrams are one of the most widely used behavioral UML diagrams. They focus on how objects (or participants) collaborate to accomplish a specific scenario or use case by showing the time-ordered exchange of messages over time. The vertical dimension represents time (top to bottom), while the horizontal axis shows the participants (lifelines).
Key elements of sequence diagrams:
- Lifeline — Vertical dashed line representing a participant (object, actor, component, service, external system). Named as :ClassName or instanceName:ClassName.
- Message — Horizontal solid arrow (synchronous call), dashed arrow (return/asynchronous reply), or open arrow (asynchronous message).
- Activation Bar (thin rectangle on lifeline) — Duration of execution/processing.
- Frame — Boxes like alt (alternative), opt (optional), loop, par (parallel), ref (reference to another interaction), sd (entire scenario).
- Actor — Stick figure for external users/systems.
- Self-message — Arrow looping back to same lifeline.
- Create/Delete — Special messages for object creation (dashed arrow with «create») and destruction (X at end of lifeline).
- Note/Constraint — Text notes or guards on messages ([condition]).
In Agile & use-case-driven projects, sequence diagrams are used to:
- Detail the main success scenario and critical alternative/exception flows of use cases
- Clarify interactions between system parts, especially integrations and APIs
- Discover missing operations on classes (automatically become method signatures)
- Identify concurrency, timing, and sequencing issues early
- Serve as basis for unit/integration tests, mocking, and API contract definition
- Communicate precisely with developers, architects, and stakeholders
Practical Examples of Sequence Diagrams in Real Projects
Here are numerous concrete examples across different domains, showing how sequence diagrams capture real interactions:
- E-commerce – Successful Checkout with Credit Card Participants: Customer (actor), :ShoppingCart, :OrderService, :PaymentGateway, :BankService Flow:
- Customer → ShoppingCart: proceedToCheckout()
- ShoppingCart → OrderService: createOrder(cartItems)
- OrderService → PaymentGateway: authorize(amount, cardDetails)
- PaymentGateway → BankService: processPayment()
- BankService –> PaymentGateway: approved
- PaymentGateway –> OrderService: authorizationToken
- OrderService → OrderService: confirmOrder() [self-message]
- OrderService –> ShoppingCart: orderConfirmed alt [payment failed] PaymentGateway –> OrderService: declined OrderService –> Customer: showError(“Payment declined”) end Practical benefit: Clearly shows synchronous call chain and failure path; used to generate mock tests for PaymentGateway.
- Mobile Banking – Secure Fund Transfer with MFA Participants: User (actor), :MobileApp, :AuthService, :CoreBankingService, :NotificationService Flow:
- User → MobileApp: initiateTransfer(destination, amount)
- MobileApp → AuthService: requestMFA()
- AuthService → NotificationService: sendOTP()
- NotificationService –> AuthService: OTP sent
- User → MobileApp: enterOTP(code)
- MobileApp → AuthService: validateOTP(code)
- AuthService –> MobileApp: valid
- MobileApp → CoreBankingService: executeTransfer(destination, amount)
- CoreBankingService → CoreBankingService: debitSource()
- CoreBankingService → CoreBankingService: creditDestination()
- CoreBankingService –> MobileApp: transferSuccessful opt [invalid OTP] AuthService –> MobileApp: invalidOTP MobileApp –> User: showRetryPrompt() end Outcome: Exposes MFA timeout and retry logic; critical for security audit.
- Ride-Sharing – Driver Accepting a Ride Request Participants: RiderApp, MatchingService, DriverApp, GPSService Flow:
- RiderApp → MatchingService: requestRide(pickup, destination)
- MatchingService → DriverApp: notifyNewRequest(rideDetails) [asynchronous]
- DriverApp → DriverApp: displayRequest()
- DriverApp → MatchingService: acceptRide()
- MatchingService → RiderApp: driverAssigned(driverInfo)
- MatchingService → GPSService: startTracking(driverLocation)
- loop [every 5s] GPSService –> MatchingService: currentLocation MatchingService –> RiderApp: updateETA() end Practical: Highlights asynchronous notifications and real-time polling loop.
- Healthcare – Booking Appointment with Conflict Check Participants: PatientPortal, AppointmentService, CalendarService, EHRService Flow:
- PatientPortal → AppointmentService: checkAvailability(doctor, dateTime)
- AppointmentService → CalendarService: querySlot()
- CalendarService –> AppointmentService: available
- AppointmentService → EHRService: verifyPatientInsurance()
- EHRService –> AppointmentService: valid
- AppointmentService → CalendarService: reserveSlot()
- CalendarService –> AppointmentService: reserved
- AppointmentService –> PatientPortal: bookingConfirmed alt [slot taken] CalendarService –> AppointmentService: conflict AppointmentService –> PatientPortal: suggestAlternatives() end Benefit: Shows parallel-like validation steps; used for integration test planning.
- Library System – Borrow Book via Self-Service Kiosk Participants: Patron (actor), :Kiosk, :LibrarySystem, :NotificationService Flow:
- Patron → Kiosk: scanCard()
- Kiosk → LibrarySystem: authenticate(memberID)
- LibrarySystem –> Kiosk: authenticated
- Patron → Kiosk: scanBook(ISBN)
- Kiosk → LibrarySystem: requestLoan(ISBN, memberID)
- LibrarySystem → LibrarySystem: checkAvailability() [self]
- LibrarySystem → LibrarySystem: checkOverdues()
- LibrarySystem –> Kiosk: loanApproved
- Kiosk –> Patron: printReceipt() opt [book not available] LibrarySystem –> Kiosk: outOfStock Kiosk –> Patron: offerReservation() end Practical: Simple yet complete for kiosk UI flow validation.
- Real-Time Stock Trading – Place Limit Order Participants: Trader (actor), :TradingPlatform, :OrderGateway, :MatchingEngine, :MarketDataFeed Flow:
- Trader → TradingPlatform: placeLimitOrder(symbol, price, quantity)
- TradingPlatform → OrderGateway: submitOrder(order)
- OrderGateway → MatchingEngine: addToOrderBook()
- MatchingEngine –> OrderGateway: accepted
- OrderGateway –> TradingPlatform: orderAcknowledged
- par [parallel] MatchingEngine → MarketDataFeed: subscribePriceUpdates(symbol) loop [price changes] MarketDataFeed –> MatchingEngine: newPrice MatchingEngine → MatchingEngine: checkForMatch() end end Outcome: Visualizes critical low-latency path and concurrent market monitoring.
In Visual Paradigm:
- Lifelines auto-populate from classes/components.
- Use combined fragments (alt, opt, loop, par) for conditional/parallel flows.
- Animate execution to walk through scenarios.
- Generate sequence from class operations or reverse from code.
- Semantic backplane links messages to class operations and use case flows.
Sequence diagrams excel at making interaction order, synchronous/asynchronous nature, and conditional behavior crystal clear—making them indispensable for detailing risky or complex use case realizations.
This prepares you for the complementary view of Communication Diagrams next, where structure takes precedence over strict timing.

