Business Model Diagram: Artifact of Vision Phase
In the fast-paced business environment, having a solid business model is crucial for long-term success. A business model is a blueprint that outlines how a business creates, delivers, and captures value. It encompasses all aspects of a business, including its customers, products, marketing strategies, revenue streams, and cost structure. However, having a good business model is not enough to guarantee success. Implementation is equally important. An implementation plan provides a structured approach to executing the business model and achieving the intended goals. In this article, we will discuss why an implementation plan is essential for improving a business model and how it can be used to drive growth and profitability.
What is a Business Model
A business model diagram is a visual representation that outlines the key components of a business model, such as the value proposition, customer segments, channels and delivery, revenue streams, and cost structure. It provides a clear and concise way to communicate the underlying logic and structure of a business model.
Business model diagrams are useful because they help entrepreneurs, managers, and investors understand how a business creates, delivers, and captures value. By breaking down a business model into its key components, a diagram can reveal areas of strength and weakness, highlight opportunities for improvement, and facilitate discussion and collaboration among stakeholders.
Additionally, a business model diagram can serve as a valuable tool for strategic planning and decision-making. It can help businesses identify potential sources of revenue and cost savings, prioritize investments and resource allocation, and evaluate the impact of new products, services, or business models.
Overall, a business model diagram is an effective way to visualize and communicate the key elements of a business model, and can help businesses create, deliver, and capture value in a more efficient and effective manner.
Business Model Canvas
The Business Model Canvas (BMC) is a strategic management tool that allows organizations to map out and analyze their business model. It is a visual template that helps entrepreneurs and business managers to understand the key components of their business and to identify areas where they can optimize their operations. The BMC is a widely used tool that is applicable to businesses of all sizes and industries.
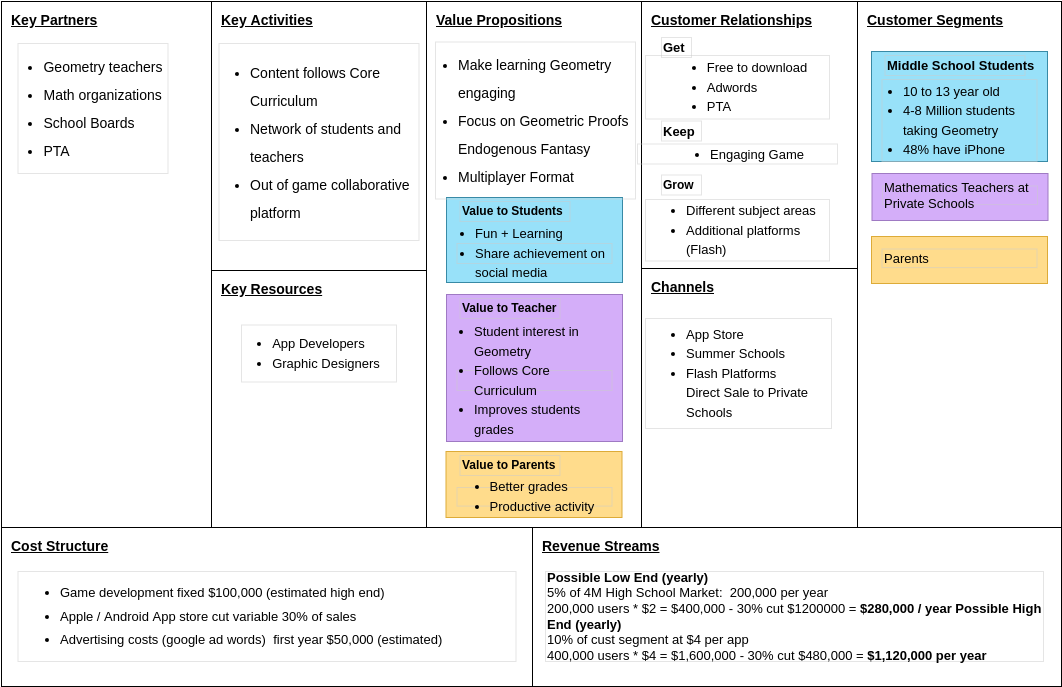
The BMC consists of nine key elements, which are arranged in a specific order on the canvas:
- Value Proposition describes the unique value that the business offers to its customers. The Value Proposition is the cornerstone of the business model and should be carefully crafted to ensure that it meets the needs of the target market.
- Customer Segments are the specific groups of customers that the business targets with its products or services. Identifying and understanding the needs of these customer segments is critical to developing an effective Value Proposition.
- Channels are the ways in which the business delivers its products or services to its customers. Channels can include both physical and digital channels, and can be direct or indirect.
- Customer Relationships describe the ways in which the business interacts with its customers. This can include everything from customer service to marketing and advertising.
- Revenue Streams are the ways in which the business generates revenue. This can include both direct and indirect revenue streams, such as sales of products or services, subscription fees, and advertising revenue.
- Key Resources are the resources that the business needs in order to operate effectively. This can include physical resources such as equipment and facilities, as well as human resources such as employees and contractors.
- Key Activities are the specific actions that the business needs to take in order to create and deliver its products or services. This can include everything from product development to marketing and sales.
- Key Partnerships are the relationships that the business has with other organizations that are critical to its success. This can include suppliers, distributors, and other strategic partners.
- Cost Structure describes the costs that the business incurs in order to operate. This can include everything from the cost of goods sold to overhead expenses.
Using the Business Model Canvas can help businesses to identify areas where they can optimize their operations and improve their profitability. By analyzing each of the nine elements of the BMC, businesses can identify areas where they can reduce costs, increase revenue, and improve the customer experience.
The Business Model Canvas is a powerful tool that can help businesses to develop a comprehensive understanding of their business model. By analyzing each of the nine elements of the canvas, businesses can identify areas where they can optimize their operations and improve their profitability. Whether you are an entrepreneur launching a new business or a business manager looking to improve your existing operations, the Business Model Canvas is a valuable tool that can help you to achieve your goals.
Example: grocery store
Problem scenario: A local grocery store is struggling to attract and retain customers due to increased competition from larger supermarkets in the area.
- Value Proposition: The grocery store needs to differentiate itself from its competitors by offering a unique value proposition that meets the needs of its target market. The store could focus on offering locally sourced produce and products, or providing personalized customer service.
- Customer Segments: The grocery store needs to identify its target market and tailor its offerings to meet their specific needs. This could include targeting health-conscious consumers or families with young children.
- Channels: The grocery store needs to leverage both physical and digital channels to reach its target market. This could include offering online ordering and delivery, as well as social media marketing and in-store promotions.
- Customer Relationships: The grocery store needs to establish strong customer relationships in order to retain customers and build loyalty. This could include offering personalized recommendations and discounts based on customers’ purchase history.
- Revenue Streams: The grocery store needs to identify multiple revenue streams to offset the impact of increased competition. This could include offering catering services or hosting events in-store.
- Key Resources: The grocery store needs to optimize its key resources to operate effectively. This could include investing in technology to streamline inventory management and reduce waste, as well as hiring and training knowledgeable staff.
- Key Activities: The grocery store needs to focus on key activities that add value to its customers and differentiate it from competitors. This could include offering cooking classes or tastings, as well as collaborating with local farmers and artisans to offer unique products.
- Key Partnerships: The grocery store needs to establish strategic partnerships with suppliers and distributors to ensure a reliable supply chain and competitive pricing. This could include working with local farmers and food producers to offer unique products, as well as partnering with third-party logistics providers to reduce delivery costs.
- Cost Structure: The grocery store needs to optimize its cost structure in order to compete with larger supermarkets. This could include reducing overhead costs by investing in energy-efficient equipment and streamlining operations to reduce labor costs.
How to Improve Your Business Model
Based on the analysis above, the areas of improvement for the local grocery store could include:
- Value Proposition: The grocery store needs to differentiate itself from its competitors by offering a unique value proposition that meets the needs of its target market. The store could focus on offering locally sourced produce and products, or providing personalized customer service.
- Customer Segments: The grocery store needs to identify its target market and tailor its offerings to meet their specific needs. This could include targeting health-conscious consumers or families with young children.
- Channels: The grocery store needs to leverage both physical and digital channels to reach its target market. This could include offering online ordering and delivery, as well as social media marketing and in-store promotions.
- Customer Relationships: The grocery store needs to establish strong customer relationships in order to retain customers and build loyalty. This could include offering personalized recommendations and discounts based on customers’ purchase history.
- Revenue Streams: The grocery store needs to identify multiple revenue streams to offset the impact of increased competition. This could include offering catering services or hosting events in-store.
- Key Resources: The grocery store needs to optimize its key resources to operate effectively. This could include investing in technology to streamline inventory management and reduce waste, as well as hiring and training knowledgeable staff.
- Key Activities: The grocery store needs to focus on key activities that add value to its customers and differentiate it from competitors. This could include offering cooking classes or tastings, as well as collaborating with local farmers and artisans to offer unique products.
- Key Partnerships: The grocery store needs to establish strategic partnerships with suppliers and distributors to ensure a reliable supply chain and competitive pricing. This could include working with local farmers and food producers to offer unique products, as well as partnering with third-party logistics providers to reduce delivery costs.
- Cost Structure: The grocery store needs to optimize its cost structure in order to compete with larger supermarkets. This could include reducing overhead costs by investing in energy-efficient equipment and streamlining operations to reduce labor costs.
The grocery store could improve by focusing on its unique value proposition and differentiating itself from competitors, optimizing its channels to reach its target market, and building strong customer relationships to retain customers and build loyalty. Additionally, the store could explore multiple revenue streams and establish strategic partnerships to ensure a reliable supply chain and competitive pricing. Finally, the store could optimize its cost structure by investing in technology to streamline operations and reduce waste.
Formulate An Implementation Plan
An implementation plan is useful for improving a business model because it provides a structured approach to implementing changes and initiatives in the business. By having a clear plan of action, stakeholders can identify areas for improvement and take proactive steps to address them.
Here’s a summary of the implementation plan in table format:
| Duration | Action | Stakeholders | Resource/Budget Required |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 weeks | Conduct customer research and identify target market segments | Grocery store owners and management, Staff, Customers | N/A |
| 2 weeks | Develop a unique value proposition based on customer research findings | Grocery store owners and management, Staff, Customers | N/A |
| 2 weeks | Develop a marketing and advertising plan to reach target market segments | Grocery store owners and management, Staff, Customers | $5,000 |
| 2 weeks | Develop partnerships with local farmers and food producers to offer unique products and improve supply chain efficiency | Grocery store owners and management, Local farmers and food producers, Third-party logistics providers | N/A |
| 4 weeks | Implement technology solutions to streamline inventory management and reduce waste | Grocery store owners and management, Staff | $10,000 |
| 2 weeks | Train and develop staff to improve customer service and provide personalized recommendations | Grocery store owners and management, Staff | $3,000 |
| 4 weeks | Host in-store events and cooking classes to build customer engagement and loyalty | Grocery store owners and management, Staff, Customers | N/A |
| 2 weeks | Evaluate the effectiveness of the implementation plan and make necessary adjustments | Grocery store owners and management, Staff | N/A |
The total budget required for the implementation plan is $18,000.
Note that:
The budget estimates provided are rough estimates and may vary depending on the specific circumstances of the online clothing store. Additionally, the people and resource requirements may vary depending on the size and complexity of the organization. It is important to regularly monitor progress towards the implementation plan and adjust as necessary to ensure that the business goals are being met.
Summary
A good business model is essential for success, but without an implementation plan, it can be difficult to achieve the desired outcomes. An implementation plan provides a roadmap for how a business will make changes and improvements to its business model. It identifies areas for improvement, outlines clear responsibilities and timelines, and ensures efficient resource allocation. By having a solid implementation plan in place, businesses can increase their chances of success and drive growth and profitability. Ultimately, an implementation plan is essential for improving a business model and achieving long-term success in today’s competitive business environment.

