Driver/Goal/Objective catalog: Artifact of Business Architecture (Phase B)
In today’s fast-paced business world, organizations face a multitude of challenges and opportunities that require them to be agile and responsive to changing market conditions. To achieve this, it is essential for organizations to have a clear understanding of their drivers, goals, and objectives, and how they align with their overall business strategy. This is where the Driver/Goal/Objective catalog comes into play. In this catalog, organizations can define their drivers, goals, and objectives, and assign measures to track progress towards achieving them. This provides a cross-organizational reference for how the organization meets its drivers in practical terms, allowing change initiatives to identify synergies and align or consolidate related change initiatives.
What is Driver/Goal/Objective Catalog
The Driver/Goal/Objective catalog is a framework used by organizations to achieve their goals by breaking them down into smaller, more manageable objectives. The purpose of this catalog is to provide a cross-organizational reference of how an organization meets its drivers (i.e., what motivates the organization to act) through goals, objectives, and (optionally) measures.

The catalog is designed to be a repository of information that lists and defines the drivers, goals, and objectives of an organization, which helps to identify the stakeholders involved and to align change initiatives across the organization. For example, if multiple organizations are attempting to achieve similar objectives, the catalog can be used to identify synergies between them and to consolidate related change initiatives.
The Driver/Goal/Objective catalog contains the following metamodel entities:
- Organization Unit: This represents a department, team, or any other organizational unit that is responsible for achieving specific objectives.
- Driver: This represents the motivation or reason behind why the organization is pursuing a particular goal. Examples of drivers could include increasing revenue, improving customer satisfaction, or reducing costs.
- Goal: This represents a specific, measurable outcome that the organization is striving to achieve. Goals are usually broad in nature and often require multiple objectives to be accomplished to achieve them.
- Objective: This represents a specific, measurable action that the organization takes to achieve a particular goal. Objectives are typically more specific and actionable than goals and are used to break down larger goals into smaller, more achievable steps.
Overall, the Driver/Goal/Objective catalog is a useful tool for organizations to manage and achieve their goals by breaking them down into smaller, more manageable pieces. It can help align change initiatives, identify stakeholders, and track progress towards achieving strategic objectives.
A Step-by-Step Guide for Developing a Driver/Goal/Objective catalog
Here’s a step-by-step guide to create a Driver/Goal/Objective catalog:
- Identify the drivers: Begin by identifying the key drivers or motivations for the organization. These could include improving revenue, increasing customer satisfaction, reducing costs, or expanding into new markets.
- Define the goals: Once the drivers are identified, define the high-level goals that the organization wants to achieve to meet these drivers. Goals should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART).
- Break down goals into objectives: Break down each goal into a set of specific, measurable objectives that will help the organization achieve the goal. Each objective should be aligned with the overall goal and contribute to its achievement.
- Assign objectives to organizational units: Assign each objective to the organizational unit responsible for achieving it. This could be a department, team, or individual responsible for the specific objective.
- Define measures: Identify the measures or key performance indicators (KPIs) that will be used to track progress towards achieving each objective. These measures should be specific, measurable, and relevant to the objective.
- Create a catalog: Organize the objectives and measures into a catalog that can be easily referenced and updated. The catalog could be a spreadsheet, database, or other tool that allows for easy searching and filtering.
- Regularly review and update the catalog: Regularly review the catalog to ensure that it remains aligned with the organization’s overall goals and objectives. Update the catalog as needed to reflect changes in the organization’s priorities, strategies, or objectives.
By following these steps, an organization can create a Driver/Goal/Objective catalog that helps to align change initiatives, identify stakeholders, and track progress towards achieving strategic objectives.
Example
Here is an example of a Driver/Goal/Objective catalog for a hypothetical company focused on improving customer satisfaction:
| Organization Unit | Driver | Goal | Objective |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sales | Increase customer satisfaction | Increase customer retention | Increase the number of customers who renew their contracts by 10% |
| Marketing | Improve product features | Increase customer satisfaction with product features | Conduct customer surveys to identify the most important product features and prioritize improvements based on customer feedback |
| Customer Service | Reduce response times | Improve customer satisfaction with support | Decrease average response times to customer inquiries from 24 hours to 12 hours |
| Product Development | Improve usability | Increase customer satisfaction with product usability | Conduct usability testing and make improvements based on feedback from at least 50% of users |
In this example, the company has identified four different organizational units, each with their own set of objectives aimed at improving customer satisfaction. The drivers identified include increasing customer satisfaction, improving product features, and reducing response times. The goals are specific outcomes related to each driver, such as increasing customer retention or improving usability, and the objectives represent specific actions the organization will take to achieve each goal, such as conducting customer surveys or reducing response times. By breaking down the overall goal of improving customer satisfaction into smaller, more specific objectives, the company can better align its change initiatives and track progress towards achieving its strategic objectives.
How to Measure
Here is the same example with an additional column for measures:
| Organization Unit | Driver | Goal | Objective | Measure |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sales | Increase customer satisfaction | Increase customer retention | Increase the number of customers who renew their contracts by 10% | Renewal rate |
| Marketing | Improve product features | Increase customer satisfaction with product features | Conduct customer surveys to identify the most important product features and prioritize improvements based on customer feedback | Customer satisfaction scores |
| Customer Service | Reduce response times | Improve customer satisfaction with support | Decrease average response times to customer inquiries from 24 hours to 12 hours | Average response time |
| Product Development | Improve usability | Increase customer satisfaction with product usability | Conduct usability testing and make improvements based on feedback from at least 50% of users | Usability score |
In this updated example, a new column for measures has been added to track progress towards achieving each objective. The measures are specific metrics or key performance indicators (KPIs) that the organization will use to assess the effectiveness of each objective. For example, in the Sales department, the measure is renewal rate, which tracks the percentage of customers who renew their contracts after the initial term. In the Marketing department, the measure is customer satisfaction scores, which will be gathered through surveys. In the Customer Service department, the measure is average response time, which will be tracked and compared against the goal of reducing response times to 12 hours. In the Product Development department, the measure is usability score, which will be based on feedback from usability testing. By tracking these measures, the organization can assess the effectiveness of each objective and make adjustments as needed to ensure progress towards achieving the overall goal of improving customer satisfaction.
A Case Study
Problem: The marketing department at a hypothetical company is struggling to improve customer engagement. They have identified several drivers for improving customer engagement, including increasing customer retention, increasing customer satisfaction, and increasing revenue from existing customers. However, they have not been able to translate these drivers into specific goals and objectives, and as a result, their efforts to improve customer engagement have been unfocused and ineffective.
Solution: To address this problem, the marketing department decides to create a Driver/Goal/Objective catalog. This catalog will provide a cross-organizational reference of how the marketing department meets its drivers in practical terms through goals, objectives, and measures.
The marketing department starts by identifying the drivers for improving customer engagement, which include increasing customer retention, increasing customer satisfaction, and increasing revenue from existing customers. They then define specific goals to achieve these drivers, such as increasing customer engagement with email campaigns, social media posts, and website content. They break down each goal into specific objectives and assign each objective to a specific team member responsible for achieving it. They also identify measures to track progress towards achieving each objective, such as email open rates, social media followers, and average time on site.
Once they have created the catalog, the marketing department regularly reviews and updates it to track progress towards achieving their objectives, identify any changes in drivers or goals, and adjust their strategies as necessary. They also share the catalog with other departments in the company to identify any synergies or areas where change initiatives can be aligned or consolidated.
By creating a Driver/Goal/Objective catalog, the marketing department is able to align their objectives with the overall drivers and goals of the company, track progress towards achieving their objectives, and identify any areas where they need to adjust their strategies to achieve their goals. This helps them improve customer engagement and achieve their business objectives.
Here’s an example of how a marketing department at a hypothetical company might create a Driver/Goal/Objective catalog to improve customer engagement:
Step 1: Identify the drivers The marketing department identifies the following drivers for improving customer engagement:
- Increase customer retention
- Increase customer satisfaction
- Increase revenue from existing customers
Step 2: Define the goals The marketing department defines the following goals to achieve these drivers:
- Increase customer engagement with email campaigns by 20%
- Increase customer engagement with social media posts by 25%
- Increase customer engagement with website content by 30%
Step 3: Break down goals into objectives The marketing department breaks down each goal into specific objectives:
Goal: Increase customer engagement with email campaigns by 20% Objectives:
- Increase email open rates by 10%
- Increase click-through rates by 10%
Goal: Increase customer engagement with social media posts by 25% Objectives:
- Increase social media followers by 15%
- Increase engagement rates on social media posts by 10%
Goal: Increase customer engagement with website content by 30% Objectives:
- Increase time spent on website by 15%
- Decrease bounce rate by 10%
Step 4: Assign objectives to organizational units The marketing department assigns each objective to a specific team member responsible for achieving it:
- Increase email open rates by 10%: Email Marketing Manager
- Increase click-through rates by 10%: Email Marketing Manager
- Increase social media followers by 15%: Social Media Manager
- Increase engagement rates on social media posts by 10%: Social Media Manager
- Increase time spent on website by 15%: Website Manager
- Decrease bounce rate by 10%: Website Manager
Step 5: Define measures The marketing department identifies the following measures to track progress towards achieving each objective:
Objective: Increase email open rates by 10% Measure: Email open rate
Objective: Increase click-through rates by 10% Measure: Click-through rate
Objective: Increase social media followers by 15% Measure: Number of social media followers
Objective: Increase engagement rates on social media posts by 10% Measure: Engagement rate on social media posts
Objective: Increase time spent on website by 15% Measure: Average time on site
Objective: Decrease bounce rate by 10% Measure: Bounce rate
Step 6: Create a catalog The marketing department creates a Driver/Goal/Objective catalog using a spreadsheet:
| Driver | Goal | Objective | Responsible Team Member | Measure |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Increase customer retention | Increase customer engagement with email campaigns by 20% | Increase email open rates by 10% | Email Marketing Manager | Email open rate |
| Increase customer retention | Increase customer engagement with email campaigns by 20% | Increase click-through rates by 10% | Email Marketing Manager | Click-through rate |
| Increase customer satisfaction | Increase customer engagement with social media posts by 25% | Increase social media followers by 15% | Social Media Manager | Number of social media followers |
| Increase customer satisfaction | Increase customer engagement with social media posts by 25% | Increase engagement rates on social media posts by 10% | Social Media Manager | Engagement rate on social media posts |
| Increase revenue from existing customers | Increase customer engagement with website content by 30% | Increase time spent on website by 15% | Website Manager | Average time on site |
| Increase revenue from existing customers | Increase customer engagement with website content by 30% | Decrease bounce rate by 10% | Website Manager | Bounce rate |
Here is the corresponding ArchiMate diagram:
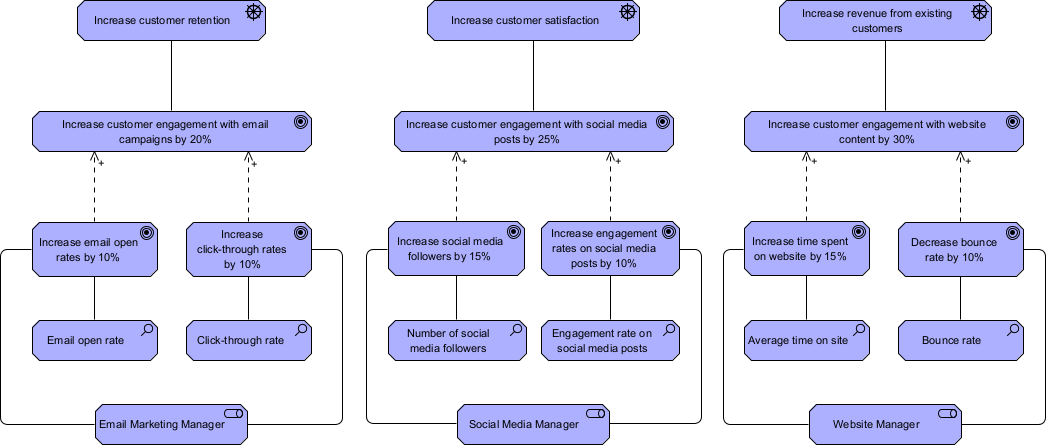
Step 7: Regularly review and update the catalog The marketing department reviews the catalog on a quarterly basis to track progress towards achieving the objectives and measures, identify any changes in drivers or goals, and adjust the catalog as necessary. They also share the catalog with other departments in the company to identify any synergies or areas where change initiatives can be aligned or consolidated.
By creating and regularly updating a Driver/Goal/Objective catalog, the marketing department is able to improve customer engagement by aligning their objectives with the overall drivers and goals of the company. They are also able to track progress towards achieving their objectives and identify any areas where they need to adjust their strategies to achieve their goals.
Summary
The Driver/Goal/Objective catalog is a powerful tool for organizations seeking to improve their agility and responsiveness in today’s fast-paced business world. By defining their drivers, goals, and objectives, and assigning measures to track progress towards achieving them, organizations can align their objectives with their overall business strategy and track progress towards achieving their goals. This enables them to identify synergies across the organization and align or consolidate related change initiatives. By regularly reviewing and updating the catalog, organizations can ensure that they remain agile and responsive to changing market conditions, while achieving their business objectives.

