Value Chain Diagram: Artifacts of Vision Phase
What is a Value Chain Diagram
A value chain diagram is a visual representation of the various activities involved in the production of a product or service. It includes all the steps from the raw materials stage to the final delivery of the product or service to the customer. The diagram shows how value is added at each step of the process and helps to identify areas where efficiencies can be gained and costs can be reduced. It is a useful tool for businesses to analyze their operations and make improvements to their supply chain management.
The purpose of a value chain diagram is to provide a clear understanding of the activities involved in creating a product or service and how value is added at each stage. It helps businesses to identify areas where they can improve their efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance value for their customers. By analyzing the value chain, businesses can identify their strengths and weaknesses and develop strategies to improve their performance. It also helps in identifying potential partners and suppliers, as well as areas where outsourcing or automation could be beneficial. Overall, the purpose of a value chain diagram is to help businesses optimize their operations and create more value for their customers.
How Value Chain Diagram Relevant to TOGAF ADM
Value chain diagrams are related to enterprise architecture frameworks like TOGAF (The Open Group Architecture Framework) in several ways. TOGAF is a comprehensive framework for enterprise architecture that includes a set of best practices, methodologies, and tools for developing and managing enterprise architecture.
One of the key components of TOGAF is the Architecture Development Method (ADM), which is a step-by-step process for developing and implementing enterprise architecture. The ADM includes various phases, such as the preliminary phase, the architecture vision phase, the business architecture phase, the information systems architecture phase, and the technology architecture phase.
Value chain diagrams can be used in several phases of the ADM to help identify the business processes, data flows, and technology systems that support the value creation activities of an organization. For example, during the business architecture phase, value chain diagrams can be used to identify the key business processes and activities that create value for the organization. During the information systems architecture phase, value chain diagrams can be used to identify the data flows and systems that support these business processes. During the technology architecture phase, value chain diagrams can be used to identify the technology infrastructure that supports the information systems.
Overall, value chain diagrams can be a useful tool for developing and implementing enterprise architecture, as they help to identify the key business processes, data flows, and technology systems that support the value creation activities of an organization.
The Structure of A Value Chain Diagram
A value chain diagram is a visual representation of the various activities involved in the production of a product or service. It includes all the steps from the raw materials stage to the final delivery of the product or service to the customer. The diagram shows how value is added at each step of the process and helps to identify areas where efficiencies can be gained and costs can be reduced. It is a useful tool for businesses to analyze their operations and make improvements to their supply chain management.
The purpose of a value chain diagram is to provide a clear understanding of the activities involved in creating a product or service and how value is added at each stage. It helps businesses to identify areas where they can improve their efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance value for their customers. By analyzing the value chain, businesses can identify their strengths and weaknesses and develop strategies to improve their performance. It also helps in identifying potential partners and suppliers, as well as areas where outsourcing or automation could be beneficial. Overall, the purpose of a value chain diagram is to help businesses optimize their operations and create more value for their customers.
How Value Chain Diagram Relevant to TOGAF ADM
Value chain diagrams are related to enterprise architecture frameworks like TOGAF (The Open Group Architecture Framework) in several ways. TOGAF is a comprehensive framework for enterprise architecture that includes a set of best practices, methodologies, and tools for developing and managing enterprise architecture.
One of the key components of TOGAF is the Architecture Development Method (ADM), which is a step-by-step process for developing and implementing enterprise architecture. The ADM includes various phases, such as the preliminary phase, the architecture vision phase, the business architecture phase, the information systems architecture phase, and the technology architecture phase.
Value chain diagrams can be used in several phases of the ADM to help identify the business processes, data flows, and technology systems that support the value creation activities of an organization. For example, during the business architecture phase, value chain diagrams can be used to identify the key business processes and activities that create value for the organization. During the information systems architecture phase, value chain diagrams can be used to identify the data flows and systems that support these business processes. During the technology architecture phase, value chain diagrams can be used to identify the technology infrastructure that supports the information systems.
Overall, value chain diagrams can be a useful tool for developing and implementing enterprise architecture, as they help to identify the key business processes, data flows, and technology systems that support the value creation activities of an organization.
The Structure of A Value Chain Diagram
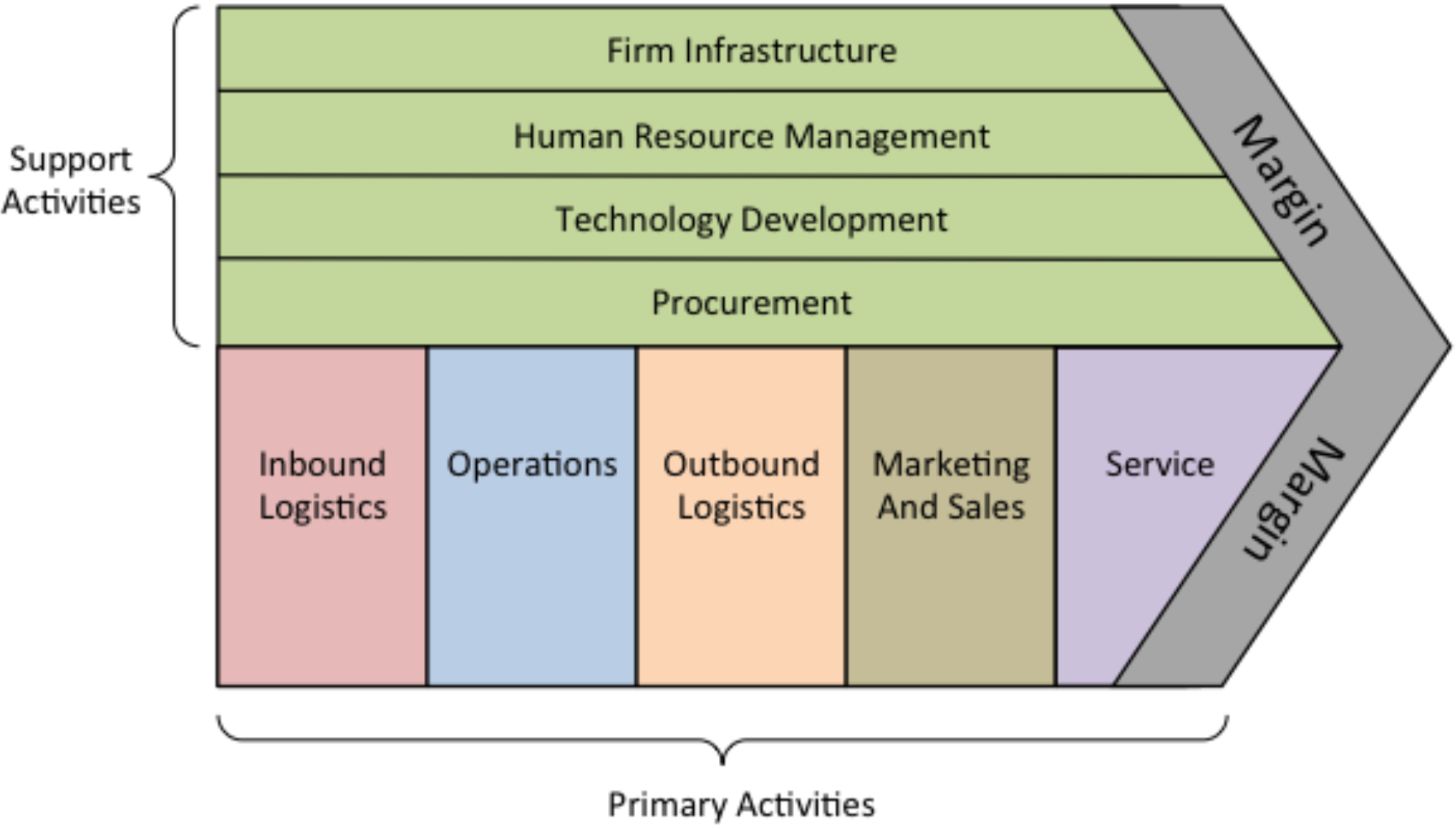
A value chain diagram typically consists of a series of activities that are involved in the creation and delivery of a product or service. The structure of a value chain diagram is usually presented in a linear format, with the activities arranged in the sequence in which they occur.
The value chain is typically divided into two main categories of activities: primary activities and support activities. Primary activities are the core activities that are directly involved in the creation and delivery of the product or service, while support activities are the activities that support the primary activities.
- The primary activities are typically broken down into several subcategories, including inbound logistics, operations, outbound logistics, marketing and sales, and service. Inbound logistics involves the receipt and storage of raw materials, while operations involve the production process. Outbound logistics involves the delivery of finished products to customers, while marketing and sales involve the promotion and sale of products. Finally, service involves providing support and after-sales service to customers.
- The support activities are also typically broken down into several subcategories, including procurement, technology development, human resource management, and infrastructure. Procurement involves the sourcing and purchasing of raw materials and supplies, while technology development involves the development of technology that supports the primary activities. Human resource management involves the management of the workforce of the organization, while infrastructure involves the management of the facilities and equipment used in the organization.
The structure of a value chain diagram is typically presented in a linear format, with the activities arranged in the sequence in which they occur. The diagram is divided into primary and support activities, and each category is further broken down into subcategories that represent the specific activities involved in the creation and delivery of a product or service.
Value Chain Diagram for a Coffee Shop
Problem Description:
The coffee shop is facing several challenges in its operations, including inefficiencies that lead to high costs and a lack of differentiation from competitors. One of the primary challenges is in the procurement of raw materials, which currently involves sourcing coffee beans, milk, and sugar from multiple suppliers. This leads to higher costs and longer lead times, which impacts the quality and freshness of the coffee and food items.
Another challenge is in the operations of the coffee shop, particularly in the roasting and brewing processes. The current processes are manual and time-consuming, leading to longer wait times for customers and inconsistencies in the quality of the coffee.
Additionally, the coffee shop is facing challenges in marketing and sales, as it lacks a strong brand identity and differentiation from competitors. This leads to difficulty in attracting and retaining customers.
Overall, the coffee shop needs to optimize its value chain to address these challenges and improve its efficiency and competitiveness. By streamlining its procurement process, investing in technology to improve its operations, and developing a strong brand identity, the coffee shop can differentiate itself from competitors and create more value for its customers.
Example
Here’s an example of the coffee shop value chain separated into primary and support activities:
Primary Activities:
- Inbound Logistics: Ordering of raw materials such as coffee beans, milk, and sugar.
- Operations: Roasting and brewing of coffee, preparation of food items, and serving of customers.
- Outbound Logistics: Delivery of coffee and food items to customers in the coffee shop.
- Marketing and Sales: Advertising and promotion of the coffee shop to attract customers.
- Service: Interacting with customers and providing excellent customer service.
Support Activities:
- Procurement: Sourcing and comparing the source of raw materials such as coffee beans, milk, and sugar.
- Technology Development: Research and development of technology that supports the primary activities, such as coffee roasting and brewing equipment.
- Human Resource Management: Managing the workforce of the coffee shop, including hiring, training, and retention of employees.
- Infrastructure: Managing the facilities and equipment used in the coffee shop, including maintenance and repair.
By analyzing the value chain in terms of primary and support activities, the coffee shop can identify areas where they can improve their efficiency and reduce costs. For example, they may identify that they can reduce their procurement costs by sourcing coffee beans directly from the growers instead of through a middleman. They may also identify that they can improve their operations by investing in technology development to improve the efficiency of their coffee roasting and brewing processes. Additionally, they may identify that they can improve their service by providing better training to their employees and investing in infrastructure improvements to enhance the customer experience.
In short, analyzing the coffee shop value chain in terms of primary and support activities provides a useful framework for identifying areas of improvement and optimizing the performance of the coffee shop.
Value Chain Diagram Example: Software Industry
Here’s another example of a value chain diagram with primary and support activities:
Value Chain Diagram for a Software Company:
Primary Activities:
- Research and Development: Developing software products and services.
- Marketing and Sales: Advertising and promotion of software products and services to attract customers.
- Customer Service: Providing customer support and after-sales service to customers.
- Operations: Delivering software products and services to customers.
Support Activities:
- Procurement: Sourcing of software components and hardware infrastructure required for software development and delivery.
- Technology Development: Research and development of technology that supports software development and delivery.
- Human Resource Management: Managing the workforce of the software company, including hiring, training, and retention of employees.
- Infrastructure: Managing the facilities and equipment used in the software company, including servers, software development tools, and office space.
By analyzing this value chain diagram, the software company can identify areas where they can improve their efficiency and reduce costs. For example, they may identify that they can improve their procurement process by sourcing software components and hardware infrastructure directly from the manufacturers instead of through a middleman. They may also identify that they can improve their operations by investing in technology development to improve the efficiency of software development and delivery processes.
Another area that the software company may identify is in marketing and sales. They may notice that they are not effectively differentiating their software products and services from competitors, which is impacting their ability to attract and retain customers. By investing in branding and marketing efforts, they can improve their competitiveness and create more value for their customers.
Overall, analyzing the value chain of a software company provides a useful framework for identifying areas of improvement and optimizing performance. By optimizing their operations, the software company can reduce costs, improve quality, and create more value for their customers.
Value Chain Diagram Example: Health Care Industry
Here’s an example of a value chain diagram in healthcare:
Value Chain Diagram for a Hospital:
Primary Activities:
- Patient Intake: Receiving and registering patients into the hospital system.
- Diagnosis and Treatment: Conducting medical tests and providing treatment to patients.
- Pharmacy: Dispensing medications to patients.
- Patient Care: Providing necessary care and support to patients during their stay in the hospital.
- Discharge: Discharging patients from the hospital and providing necessary follow-up instructions.
Support Activities:
- Procurement: Sourcing of medical equipment, supplies, and drugs required for hospital operations.
- Technology Development: Research and development of technology that supports medical diagnosis and treatment.
- Human Resource Management: Managing the workforce of the hospital, including hiring, training, and retention of employees.
- Infrastructure: Managing the facilities and equipment used in the hospital, including medical equipment, hospital beds, and office space.
By analyzing this value chain diagram, the hospital can identify areas where they can improve their efficiency and reduce costs. For example, they may identify that they can improve their procurement process by sourcing medical equipment and supplies directly from the manufacturers instead of through a middleman. They may also identify that they can improve their operations by investing in technology development to improve the efficiency of medical diagnosis and treatment processes.
Another area that the hospital may identify is in patient care. They may notice that they are not providing enough support to patients during their stay in the hospital, which is impacting their patient satisfaction and recovery rates. By investing in patient care initiatives and improving the quality of care, they can improve patient satisfaction and clinical outcomes.
Overall, analyzing the value chain of a hospital provides a useful framework for identifying areas of improvement and optimizing performance. By optimizing their operations, the hospital can reduce costs, improve quality, and create more value for their patients.
Using Value Chain Analysis for Business Improvement
Value chain analysis is a valuable tool for businesses seeking to improve their operations. By analyzing the value chain, companies can identify areas that need improvement and implement solutions to optimize their operations, reduce costs, and improve quality. There are several ways that businesses can use value chain analysis to improve their operations, including:
- Streamlining operations: Through value chain analysis, businesses can identify bottlenecks and inefficiencies in their operations, allowing them to streamline processes and reduce costs. This may involve optimizing production processes, improving supply chain management, or minimizing waste.
- Enhancing quality: Value chain analysis can help businesses pinpoint areas where the quality of their products or services can be improved. By investing in new technology or equipment, improving employee training, or enhancing quality control processes, businesses can improve the quality of their offerings.
- Adding customer value: Value chain analysis can reveal opportunities for businesses to increase customer value. By identifying areas where they can offer new products or services, improve customer service, or provide faster delivery times, companies can enhance their offerings and attract new customers.
Value chain analysis is a valuable tool for businesses seeking to improve their operations and gain a competitive advantage in the marketplace. Here is an example of a value chain diagram for a clothing manufacturing company:
Primary activities:
- Raw material procurement: Sourcing the raw materials, such as fabric, buttons, and zippers, from suppliers.
- Design: Creating and developing new clothing designs.
- Production: Turning raw materials into finished clothing products.
- Marketing and sales: Promoting and selling the clothing products to retailers and consumers.
- Distribution: Delivering the clothing products to retail stores or directly to customers.
Support activities:
- Research and development: Conducting market research and developing new manufacturing techniques.
- Human resource management: Recruiting, training, and managing employees.
- Information technology: Managing the company’s technological infrastructure, including its website and inventory management system.
- Procurement: Sourcing non-production goods and services such as office supplies.
- Infrastructure: Maintaining the physical infrastructure, such as buildings and machinery.
By mapping out the various stages of the value chain and identifying areas for improvement, such as streamlining the production process or optimizing the supply chain, the clothing manufacturing company can increase efficiency, reduce costs, and ultimately increase profitability.
The findings from the analysis of a value chain diagram can be used by various stakeholders in a business, including managers, executives, and employees. For example:
- Managers can use the findings to identify areas for improvement and to optimize the value chain, reducing costs, increasing efficiency, and improving quality.
- Executives can use the findings to make strategic decisions about the company’s future direction, including investments in new technologies, changes to the product line, or shifts in the target market.
- Employees can use the findings to understand their role in the value chain and to identify ways to improve their own performance and contribute to the company’s success.
In addition to internal stakeholders, the findings from a value chain analysis can also be used by external stakeholders, such as investors, customers, and suppliers, to gain insight into the company’s operations and performance.
Improvement Proposal and Action Plan
Here is an example proposal for business improvement based on the value chain analysis for a clothing manufacturing company:
Proposal:
Improving Production Efficiency through Value Chain Analysis
Problem:
The value chain analysis has revealed that the production process is taking longer than necessary, which is increasing costs and reducing efficiency.
Solution:
To address this problem, we propose conducting a thorough analysis of the production process to identify bottlenecks and inefficiencies. Based on the findings, we recommend implementing the following solution:
- Invest in new machinery and equipment to improve production efficiency
- Reorganize the production line to reduce bottlenecks and increase throughput
- Improve communication and coordination between different departments involved in the production process to reduce delays and errors
- Train employees to use new equipment and follow new procedures
- Monitor and evaluate the impact of the changes to ensure they are achieving the desired results.
Benefits:
By implementing these solutions, we anticipate the following benefits:
- Increased production efficiency and throughput
- Reduction in production costs
- Improved product quality
- Increased customer satisfaction through faster delivery times
- Competitive advantage through improved operations and enhanced customer value.
Action Plan:
To implement these solutions, we recommend the following action plan:
- Conduct a thorough analysis of the production process to identify bottlenecks and inefficiencies
- Develop a plan to invest in new machinery and equipment
- Reorganize the production line to reduce bottlenecks and increase throughput
- Develop a plan to improve communication and coordination between different departments involved in the production process
- Develop a training program to teach employees how to use new equipment and follow new procedures
- Monitor and evaluate the impact of the changes to ensure they are achieving the desired results.
Overall, by improving production efficiency through value chain analysis, we anticipate significant benefits for our clothing manufacturing company, including increased efficiency, reduced costs, improved quality, and enhanced customer satisfaction.
Summary
A value chain diagram is a visual representation of the various activities involved in the production of a product or service. It includes primary activities that are directly involved in the creation and delivery of a product or service, as well as support activities that are necessary to support the primary activities. Value chain diagrams are used by businesses to identify areas where they can improve their efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance value for their customers. They are related to enterprise architecture frameworks like TOGAF, as they can be used to develop and implement enterprise architecture strategies. By analyzing the value chain, businesses can optimize their operations and create more value for their customers.
are typically broken down into several subcategories, including inbound logistics, operations, outbound logistics, marketing and sales, and service. Inbound logistics involves the receipt and storage of raw materials, while operations involve the production process. Outbound logistics involves the delivery of finished products to customers, while marketing and sales involve the promotion and sale of products. Finally, service involves providing support and after-sales service to customers.
- The support activities are also typically broken down into several subcategories, including procurement, technology development, human resource management, and infrastructure. Procurement involves the sourcing and purchasing of raw materials and supplies, while technology development involves the development of technology that supports the primary activities. Human resource management involves the management of the workforce of the organization, while infrastructure involves the management of the facilities and equipment used in the organization.
The structure of a value chain diagram is typically presented in a linear format, with the activities arranged in the sequence in which they occur. The diagram is divided into primary and support activities, and each category is further broken down into subcategories that represent the specific activities involved in the creation and delivery of a product or service.

Value Chain Diagram for a Coffee Shop
Problem Description:
The coffee shop is facing several challenges in its operations, including inefficiencies that lead to high costs and a lack of differentiation from competitors. One of the primary challenges is in the procurement of raw materials, which currently involves sourcing coffee beans, milk, and sugar from multiple suppliers. This leads to higher costs and longer lead times, which impacts the quality and freshness of the coffee and food items.
Another challenge is in the operations of the coffee shop, particularly in the roasting and brewing processes. The current processes are manual and time-consuming, leading to longer wait times for customers and inconsistencies in the quality of the coffee.
Additionally, the coffee shop is facing challenges in marketing and sales, as it lacks a strong brand identity and differentiation from competitors. This leads to difficulty in attracting and retaining customers.
Overall, the coffee shop needs to optimize its value chain to address these challenges and improve its efficiency and competitiveness. By streamlining its procurement process, investing in technology to improve its operations, and developing a strong brand identity, the coffee shop can differentiate itself from competitors and create more value for its customers.
Example
Here’s an example of the coffee shop value chain separated into primary and support activities:
Primary Activities:
- Inbound Logistics: Ordering of raw materials such as coffee beans, milk, and sugar.
- Operations: Roasting and brewing of coffee, preparation of food items, and serving of customers.
- Outbound Logistics: Delivery of coffee and food items to customers in the coffee shop.
- Marketing and Sales: Advertising and promotion of the coffee shop to attract customers.
- Service: Interacting with customers and providing excellent customer service.
Support Activities:
- Procurement: Sourcing and comparing the source of raw materials such as coffee beans, milk, and sugar.
- Technology Development: Research and development of technology that supports the primary activities, such as coffee roasting and brewing equipment.
- Human Resource Management: Managing the workforce of the coffee shop, including hiring, training, and retention of employees.
- Infrastructure: Managing the facilities and equipment used in the coffee shop, including maintenance and repair.
By analyzing the value chain in terms of primary and support activities, the coffee shop can identify areas where they can improve their efficiency and reduce costs. For example, they may identify that they can reduce their procurement costs by sourcing coffee beans directly from the growers instead of through a middleman. They may also identify that they can improve their operations by investing in technology development to improve the efficiency of their coffee roasting and brewing processes. Additionally, they may identify that they can improve their service by providing better training to their employees and investing in infrastructure improvements to enhance the customer experience.
In short, analyzing the coffee shop value chain in terms of primary and support activities provides a useful framework for identifying areas of improvement and optimizing the performance of the coffee shop.
Value Chain Diagram Example: Software Industry
Here’s another example of a value chain diagram with primary and support activities:
Value Chain Diagram for a Software Company:
Primary Activities:
- Research and Development: Developing software products and services.
- Marketing and Sales: Advertising and promotion of software products and services to attract customers.
- Customer Service: Providing customer support and after-sales service to customers.
- Operations: Delivering software products and services to customers.
Support Activities:
- Procurement: Sourcing of software components and hardware infrastructure required for software development and delivery.
- Technology Development: Research and development of technology that supports software development and delivery.
- Human Resource Management: Managing the workforce of the software company, including hiring, training, and retention of employees.
- Infrastructure: Managing the facilities and equipment used in the software company, including servers, software development tools, and office space.
By analyzing this value chain diagram, the software company can identify areas where they can improve their efficiency and reduce costs. For example, they may identify that they can improve their procurement process by sourcing software components and hardware infrastructure directly from the manufacturers instead of through a middleman. They may also identify that they can improve their operations by investing in technology development to improve the efficiency of software development and delivery processes.
Another area that the software company may identify is in marketing and sales. They may notice that they are not effectively differentiating their software products and services from competitors, which is impacting their ability to attract and retain customers. By investing in branding and marketing efforts, they can improve their competitiveness and create more value for their customers.
Overall, analyzing the value chain of a software company provides a useful framework for identifying areas of improvement and optimizing performance. By optimizing their operations, the software company can reduce costs, improve quality, and create more value for their customers.
Value Chain Diagram Example: Health Care Industry
Here’s an example of a value chain diagram in healthcare:
Value Chain Diagram for a Hospital:
Primary Activities:
- Patient Intake: Receiving and registering patients into the hospital system.
- Diagnosis and Treatment: Conducting medical tests and providing treatment to patients.
- Pharmacy: Dispensing medications to patients.
- Patient Care: Providing necessary care and support to patients during their stay in the hospital.
- Discharge: Discharging patients from the hospital and providing necessary follow-up instructions.
Support Activities:
- Procurement: Sourcing of medical equipment, supplies, and drugs required for hospital operations.
- Technology Development: Research and development of technology that supports medical diagnosis and treatment.
- Human Resource Management: Managing the workforce of the hospital, including hiring, training, and retention of employees.
- Infrastructure: Managing the facilities and equipment used in the hospital, including medical equipment, hospital beds, and office space.
By analyzing this value chain diagram, the hospital can identify areas where they can improve their efficiency and reduce costs. For example, they may identify that they can improve their procurement process by sourcing medical equipment and supplies directly from the manufacturers instead of through a middleman. They may also identify that they can improve their operations by investing in technology development to improve the efficiency of medical diagnosis and treatment processes.
Another area that the hospital may identify is in patient care. They may notice that they are not providing enough support to patients during their stay in the hospital, which is impacting their patient satisfaction and recovery rates. By investing in patient care initiatives and improving the quality of care, they can improve patient satisfaction and clinical outcomes.
Overall, analyzing the value chain of a hospital provides a useful framework for identifying areas of improvement and optimizing performance. By optimizing their operations, the hospital can reduce costs, improve quality, and create more value for their patients.
Using Value Chain Analysis for Business Improvement
Value chain analysis is a valuable tool for businesses seeking to improve their operations. By analyzing the value chain, companies can identify areas that need improvement and implement solutions to optimize their operations, reduce costs, and improve quality. There are several ways that businesses can use value chain analysis to improve their operations, including:
- Streamlining operations: Through value chain analysis, businesses can identify bottlenecks and inefficiencies in their operations, allowing them to streamline processes and reduce costs. This may involve optimizing production processes, improving supply chain management, or minimizing waste.
- Enhancing quality: Value chain analysis can help businesses pinpoint areas where the quality of their products or services can be improved. By investing in new technology or equipment, improving employee training, or enhancing quality control processes, businesses can improve the quality of their offerings.
- Adding customer value: Value chain analysis can reveal opportunities for businesses to increase customer value. By identifying areas where they can offer new products or services, improve customer service, or provide faster delivery times, companies can enhance their offerings and attract new customers.
Value chain analysis is a valuable tool for businesses seeking to improve their operations and gain a competitive advantage in the marketplace. Here is an example of a value chain diagram for a clothing manufacturing company:
Primary activities:
- Raw material procurement: Sourcing the raw materials, such as fabric, buttons, and zippers, from suppliers.
- Design: Creating and developing new clothing designs.
- Production: Turning raw materials into finished clothing products.
- Marketing and sales: Promoting and selling the clothing products to retailers and consumers.
- Distribution: Delivering the clothing products to retail stores or directly to customers.
Support activities:
- Research and development: Conducting market research and developing new manufacturing techniques.
- Human resource management: Recruiting, training, and managing employees.
- Information technology: Managing the company’s technological infrastructure, including its website and inventory management system.
- Procurement: Sourcing non-production goods and services such as office supplies.
- Infrastructure: Maintaining the physical infrastructure, such as buildings and machinery.
By mapping out the various stages of the value chain and identifying areas for improvement, such as streamlining the production process or optimizing the supply chain, the clothing manufacturing company can increase efficiency, reduce costs, and ultimately increase profitability.
The findings from the analysis of a value chain diagram can be used by various stakeholders in a business, including managers, executives, and employees. For example:
- Managers can use the findings to identify areas for improvement and to optimize the value chain, reducing costs, increasing efficiency, and improving quality.
- Executives can use the findings to make strategic decisions about the company’s future direction, including investments in new technologies, changes to the product line, or shifts in the target market.
- Employees can use the findings to understand their role in the value chain and to identify ways to improve their own performance and contribute to the company’s success.
In addition to internal stakeholders, the findings from a value chain analysis can also be used by external stakeholders, such as investors, customers, and suppliers, to gain insight into the company’s operations and performance.
Improvement Proposal and Action Plan
Here is an example proposal for business improvement based on the value chain analysis for a clothing manufacturing company:
Proposal:
Improving Production Efficiency through Value Chain Analysis
Problem:
The value chain analysis has revealed that the production process is taking longer than necessary, which is increasing costs and reducing efficiency.
Solution:
To address this problem, we propose conducting a thorough analysis of the production process to identify bottlenecks and inefficiencies. Based on the findings, we recommend implementing the following solution:
- Invest in new machinery and equipment to improve production efficiency
- Reorganize the production line to reduce bottlenecks and increase throughput
- Improve communication and coordination between different departments involved in the production process to reduce delays and errors
- Train employees to use new equipment and follow new procedures
- Monitor and evaluate the impact of the changes to ensure they are achieving the desired results.
Benefits:
By implementing these solutions, we anticipate the following benefits:
- Increased production efficiency and throughput
- Reduction in production costs
- Improved product quality
- Increased customer satisfaction through faster delivery times
- Competitive advantage through improved operations and enhanced customer value.
Action Plan:
To implement these solutions, we recommend the following action plan:
- Conduct a thorough analysis of the production process to identify bottlenecks and inefficiencies
- Develop a plan to invest in new machinery and equipment
- Reorganize the production line to reduce bottlenecks and increase throughput
- Develop a plan to improve communication and coordination between different departments involved in the production process
- Develop a training program to teach employees how to use new equipment and follow new procedures
- Monitor and evaluate the impact of the changes to ensure they are achieving the desired results.
Overall, by improving production efficiency through value chain analysis, we anticipate significant benefits for our clothing manufacturing company, including increased efficiency, reduced costs, improved quality, and enhanced customer satisfaction.
Summary
A value chain diagram is a visual representation of the various activities involved in the production of a product or service. It includes primary activities that are directly involved in the creation and delivery of a product or service, as well as support activities that are necessary to support the primary activities. Value chain diagrams are used by businesses to identify areas where they can improve their efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance value for their customers. They are related to enterprise architecture frameworks like TOGAF, as they can be used to develop and implement enterprise architecture strategies. By analyzing the value chain, businesses can optimize their operations and create more value for their customers.

