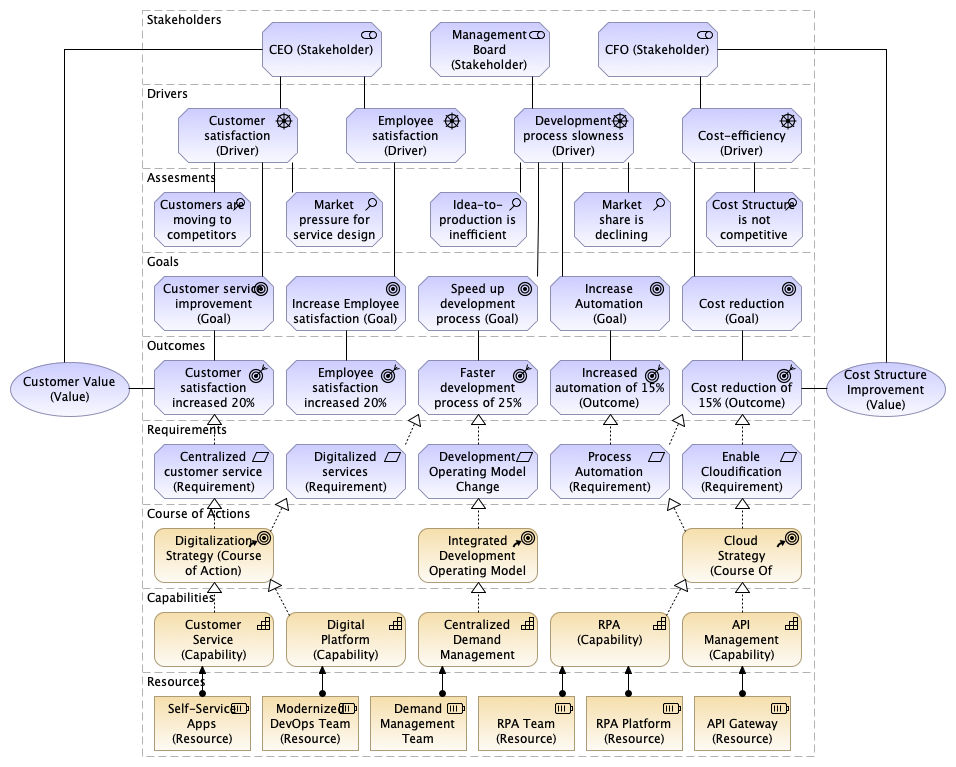
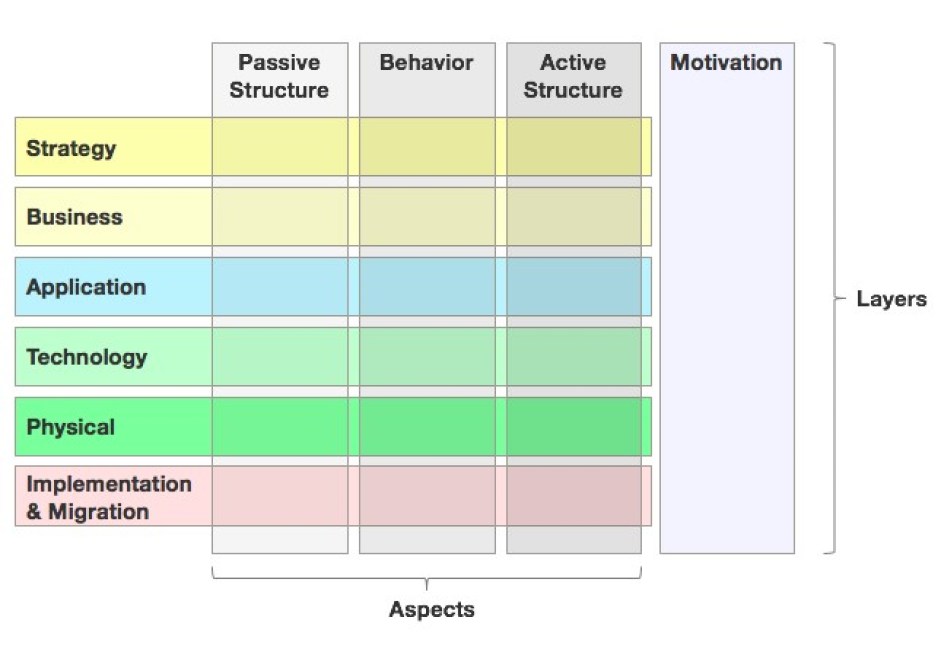
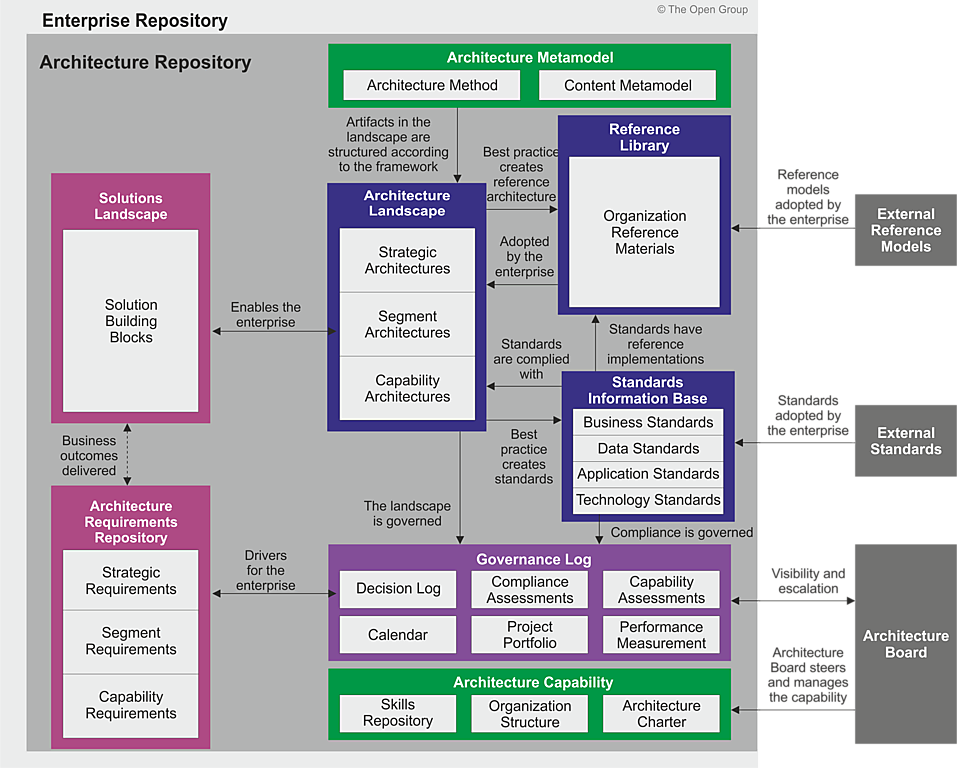
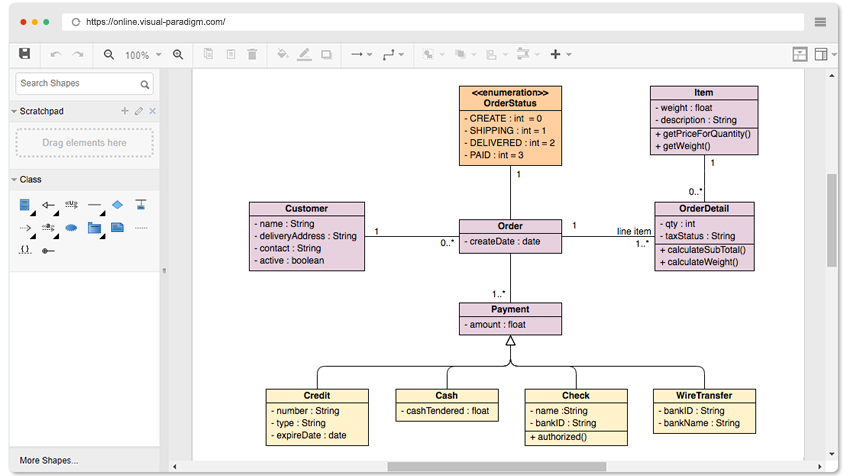
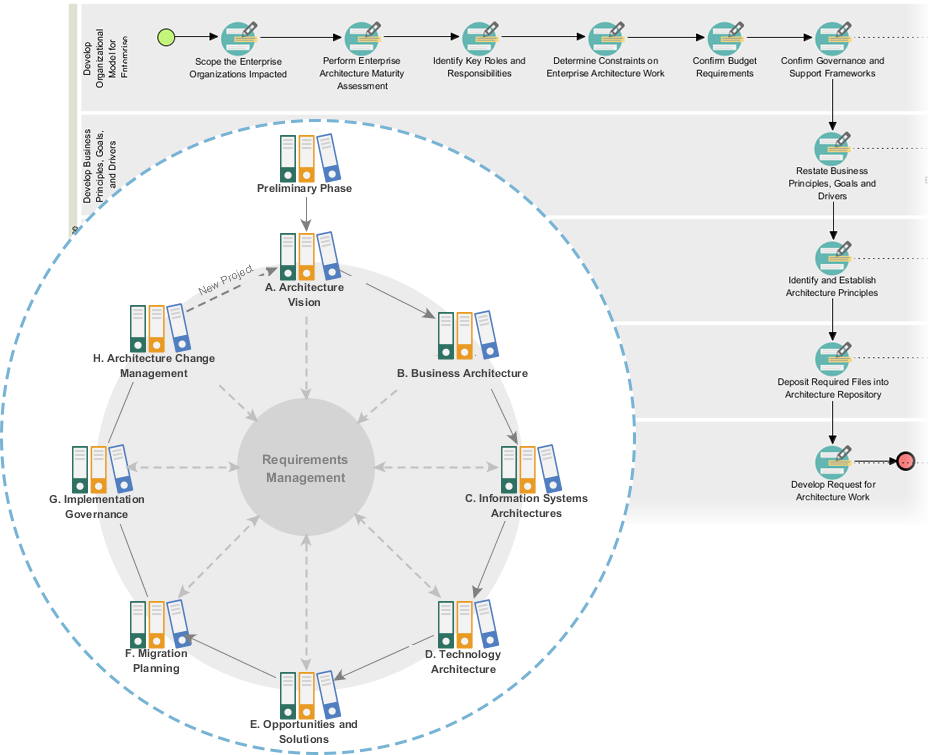
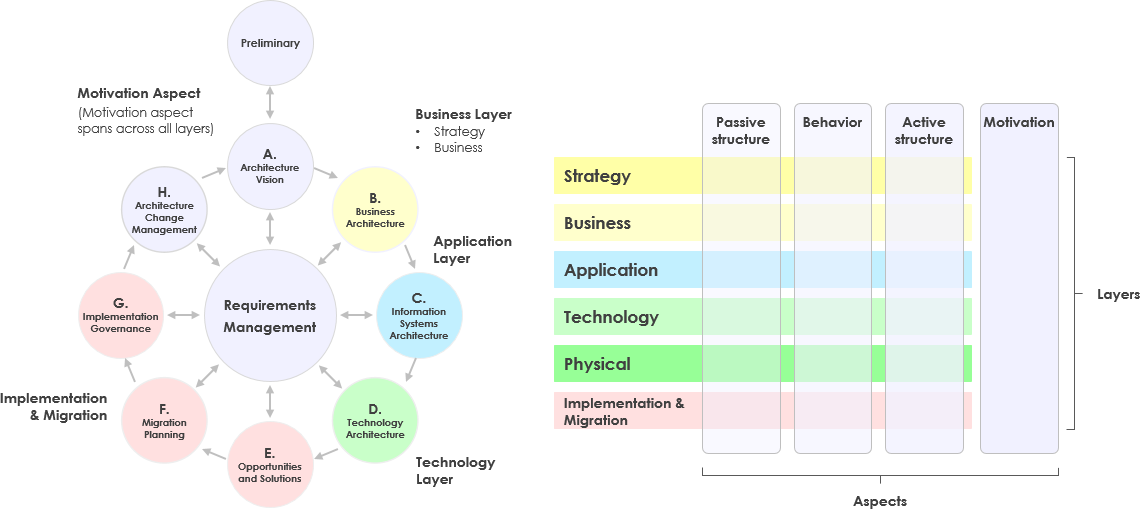
Introduction to ArchiMate Risk Analysis View for Enterprise Architecture
The Risk Analysis View in ArchiMate helps in identifying, assessing, and managing risks within an organization. This view is crucial for aligning IT security measures with business goals and ensuring compliance with standards like ISOIntroduction to ArchiMate Risk Analysis View for Enterprise Architecture