Introduction
Project management is a critical discipline in today’s business and organizational landscape, aiming to achieve specific goals within defined constraints. To streamline project management practices and provide a standardized framework for professionals, the Project Management Institute (PMI) introduced the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK). In this article, we’ll delve into what PMBOK is, how it aids project management, and how it compares to other similar approaches.
What is PMBOK?
PMBOK, an acronym for the Project Management Body of Knowledge, is a comprehensive guidebook developed by PMI, a globally recognized organization dedicated to advancing the field of project management. PMBOK is not a methodology in itself but rather a collection of best practices, standards, and guidelines that encompass the fundamental principles and concepts of project management.
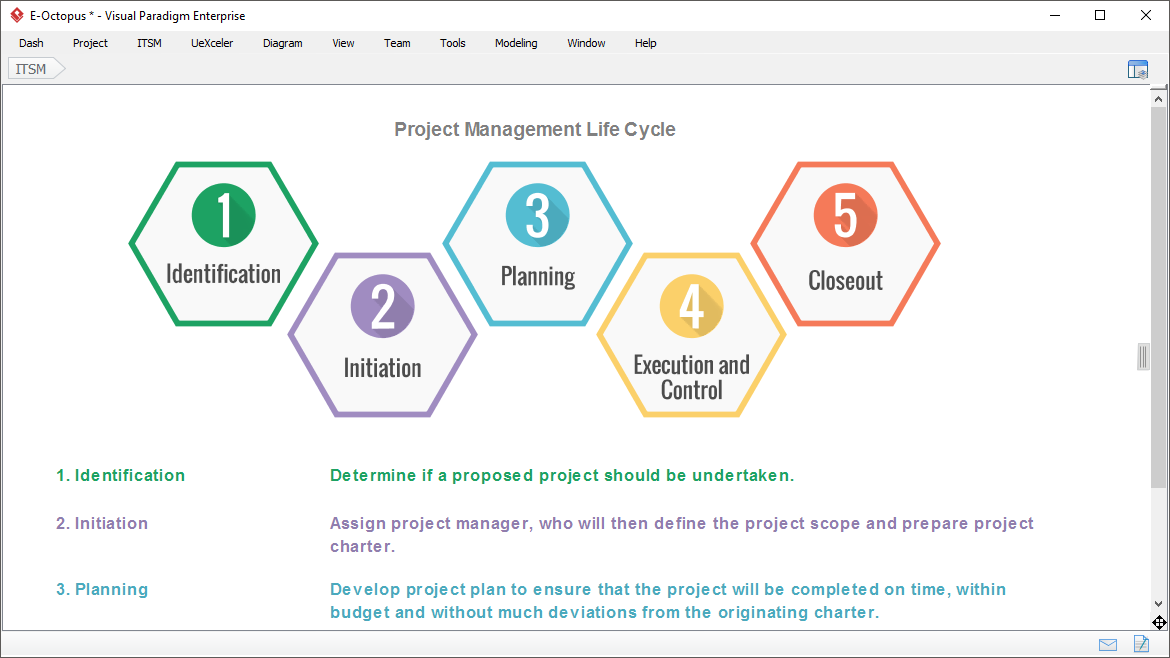
How Does PMBOK Help in Project Management?
- Standardization: PMBOK provides a standardized and systematic approach to project management, ensuring that professionals across different industries and sectors have a common language and framework to work with.
- Knowledge Repository: PMBOK serves as a repository of knowledge, encompassing the latest trends, tools, and techniques in project management. It helps project managers stay up-to-date with industry best practices.
- Process-Oriented: PMBOK outlines a set of interconnected processes that guide project management activities from initiation to closure. This process-driven approach helps in maintaining control and ensuring consistency throughout a project’s lifecycle.
- Best Practices: PMBOK incorporates globally recognized best practices in project management. By following these practices, organizations can enhance project success rates, reduce risks, and improve project outcomes.
- Common Terminology: PMBOK defines and standardizes terminology, reducing confusion and misunderstandings among project stakeholders. This clarity aids communication and collaboration within project teams.
Comparing PMBOK to Other Similar Approaches
While PMBOK is a widely used and respected project management framework, there are other methodologies and approaches that professionals can consider. Here’s a comparison of PMBOK to a few prominent alternatives:
- Agile: Agile methodologies, such as Scrum and Kanban, emphasize flexibility, iterative development, and customer collaboration. PMBOK is more process-oriented and traditional, while Agile is adaptive and customer-centric. The choice depends on the project’s nature and requirements.
- PRINCE2 (PRojects IN Controlled Environments): PRINCE2 is a process-driven project management framework that, like PMBOK, provides a structured approach. PRINCE2 is often favored in certain industries and countries, while PMBOK is more internationally recognized.
- Waterfall: The Waterfall model is a sequential and linear approach to project management, where each phase must be completed before moving to the next. PMBOK offers more flexibility and adaptability compared to the Waterfall model, which is highly structured.
- Lean Six Sigma: Lean Six Sigma focuses on process improvement and minimizing waste. While it can be integrated with PMBOK, it is primarily used for optimizing processes within a project or organization.
Summarizing Different Project Management Approaches
It’s important to note that the choice of project management approach should align with the specific project’s characteristics, organizational culture, and stakeholder preferences. Many organizations also adopt hybrid approaches that combine elements from different
Here’s a table contrasting the pros and cons of various project management approaches in different aspects:
| Aspect | PMBOK | Agile | PRINCE2 | Waterfall | Lean Six Sigma |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flexibility | Limited flexibility due to its | Highly flexible and adaptive, | Moderate flexibility with the | Limited flexibility as it follows | Limited flexibility, mainly focused |
| process-driven nature. | allows for changes throughout the | ability to tailor processes to the | a sequential and rigid approach. | on process improvement. | |
| Customer Focus | Customer satisfaction is important, | Customer collaboration is | Emphasizes business justification | Limited customer involvement until | Customer needs are addressed through |
| but less emphasis on real-time | prioritized, and feedback is | and continuous business benefits. | project completion. | process improvement. | |
| Complexity Handling | Suitable for complex projects with | Effective for complex projects, | Effective for projects of varying | Best suited for projects with well- | Effective for process optimization |
| structured processes and controls. | especially those with evolving | sizes and complexities. | defined requirements and minimal | and waste reduction, not for complex | |
| requirements. | changes. | project management. | |||
| Phases & Planning | Extensive documentation and planning | Adaptive planning, minimal initial | Detailed planning and documentation | Thorough planning and documentation, | Focuses on process mapping and |
| are required before execution. | planning, and planning evolves as | from the outset, with stage | execution follows a predetermined | statistical analysis rather than | |
| the project progresses. | boundaries. | path. | project phases. | ||
| Risk Management | Comprehensive risk management | Ongoing risk assessment and | Risk management is integrated into | Risk assessment is typically done | Risk management is a core component |
| framework with risk registers and | adaptation to changing conditions. | the methodology, but may not be as | at the project’s outset, but not | but is limited to process improvement. | |
| mitigation strategies. | detailed as in PMBOK. | continuously throughout. | |||
| Documentation | Extensive documentation required, | Emphasizes working software | Documentation is structured and | Detailed documentation at each phase | Comprehensive documentation of |
| which can be time-consuming. | over comprehensive documentation. | mandatory, which can be burdensome. | of the project lifecycle. | processes, procedures, and outcomes. | |
| Change Management | Change control processes are robust | Embraces change and welcomes it | Change control is part of the | Change is typically discouraged or | Change management principles are |
| and can slow down project progress. | as a way to improve the product. | methodology, allowing controlled | requires formal procedures. | applied for continuous improvement. |
Conclusion
PMBOK is a valuable resource for project managers and organizations seeking a structured and standardized approach to project management. It offers a comprehensive set of best practices, processes, and guidelines that can enhance project success. However, the choice of project management approach should always consider the specific needs of the project, industry standards, and the organization’s culture. Depending on the project’s complexity and requirements, professionals may choose to combine elements of PMBOK with other methodologies or opt for a more specialized approach like Agile or PRINCE2. Ultimately, effective project management relies on selecting the right tools and methodologies for the job.



