In TOGAF, the Architecture Repository is a key component of the Architecture Development Method (ADM) and it is a managed repository that stores all the architectural information, models, and artifacts that are created during the ADM. The Architecture Repository consists of several different classes of architectural information, which are:
- Architecture Metamodel – describes the organizationally tailored application of an architecture framework, including a method for architecture development and a metamodel for architecture content
- Architecture Capability – defines the parameters, structures, and processes that support governance of the Architecture Repository
- Architecture Landscape – presents an architectural representation of assets in use, or planned, by the enterprise at particular points in time
- Standards Information Base – captures the standards with which new architectures must comply, which may include industry standards, selected products and services from suppliers, or shared services already deployed within the organization
- Reference Library – provides guidelines, templates, patterns, and other forms of reference material that can be leveraged in order to accelerate the creation of new architectures for the enterprise
- Governance Log – provides a record of governance activity across the enterprise
- Architecture Requirements Repository – provides a view of all authorized architecture requirements which have been agreed with the Architecture Board
- Solutions Landscape – presents an architectural representation of the Solution Building Blocks (SBBs) supporting the Architecture Landscape which have been planned or deployed by the enterprise
Each of these classes of information serves a specific purpose in the ADM and provides a comprehensive view of the enterprise architecture. The Architecture Repository is used throughout the ADM to store and manage the various artifacts created during each phase, and to provide a central location for architects and stakeholders to access and share information.
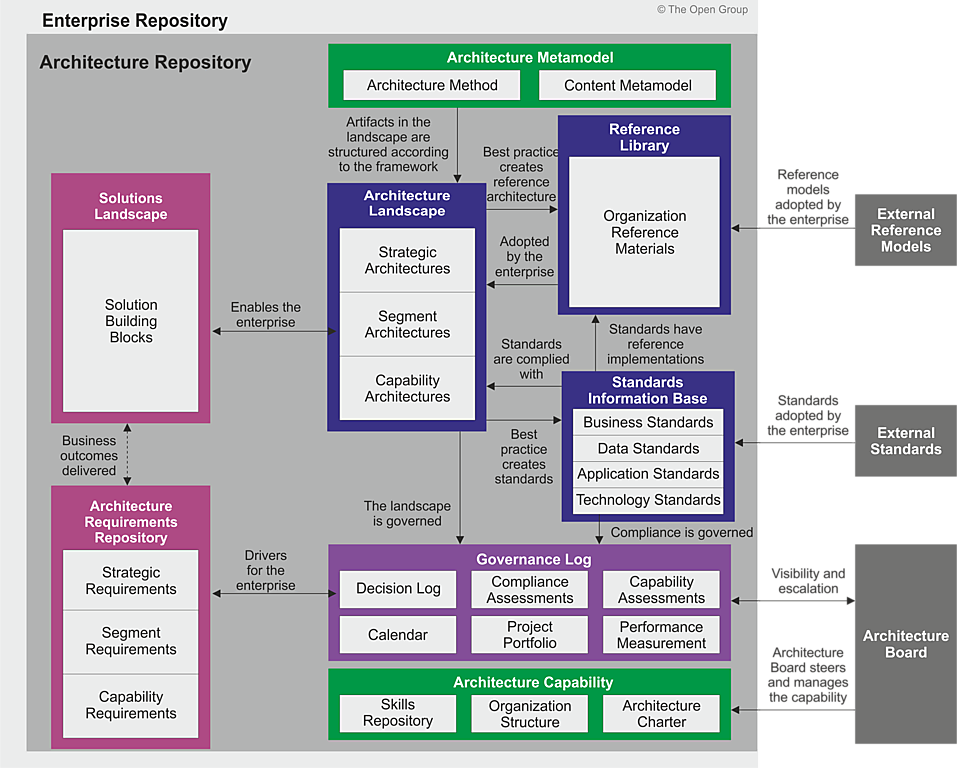
Difference Classes of Architectural information
As mentioned above, the Architecture Repository consists of several different classes of architectural information
Architecture Metamodel
In the TOGAF framework, the Architecture Metamodel is composed of two parts: the Architecture Method and the Content Metamodel.
- The Architecture Method describes the process for developing and managing the architecture within an organization. It includes various phases and steps for developing and implementing an enterprise architecture. The Architecture Method is designed to be flexible and adaptable to different organizations and their unique needs.
- The Content Metamodel provides a framework for organizing and structuring the architecture content, including the building blocks, artifacts, and deliverables that are produced during the architecture development process. It defines the structure, relationships, and attributes of the architecture content, and provides a common language and vocabulary for describing and communicating the architecture.
Together, the Architecture Method and the Content Metamodel form a comprehensive framework for developing and managing enterprise architecture within an organization.
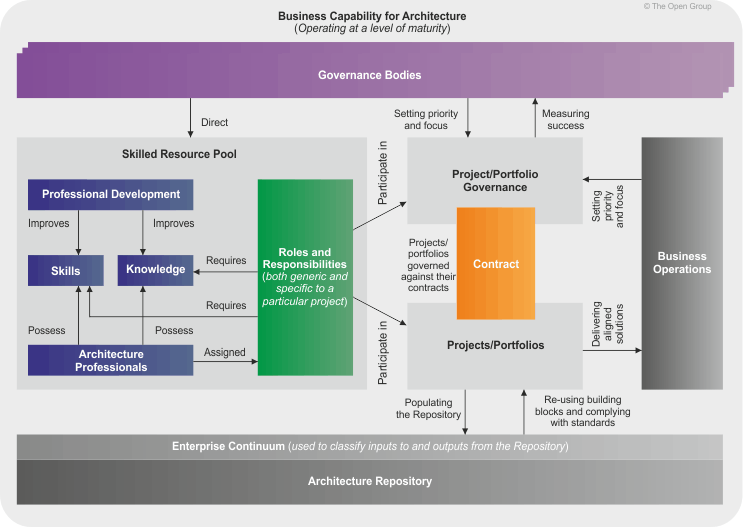
Architecture Capability
In the TOGAF framework, the Architecture Capability is defined as the set of organizational resources and processes that support the development and management of the enterprise architecture.
One of the key components of the Architecture Capability is the Architecture Repository, which is a structured collection of all architecture artifacts and building blocks within an organization. The Architecture Capability defines the parameters, structures, and processes that support the governance of the Architecture Repository.
Governance of the Architecture Repository involves establishing policies, procedures, and standards for the creation, maintenance, and use of the architecture artifacts and building blocks. It also involves defining roles and responsibilities for the various stakeholders involved in the architecture development and management process.
In addition to governance of the Architecture Repository, the Architecture Capability includes other key components such as architecture governance, architecture content framework, and architecture skills and competencies. These components work together to support the development and management of a robust and effective enterprise architecture that aligns with the business goals and objectives of the organization.
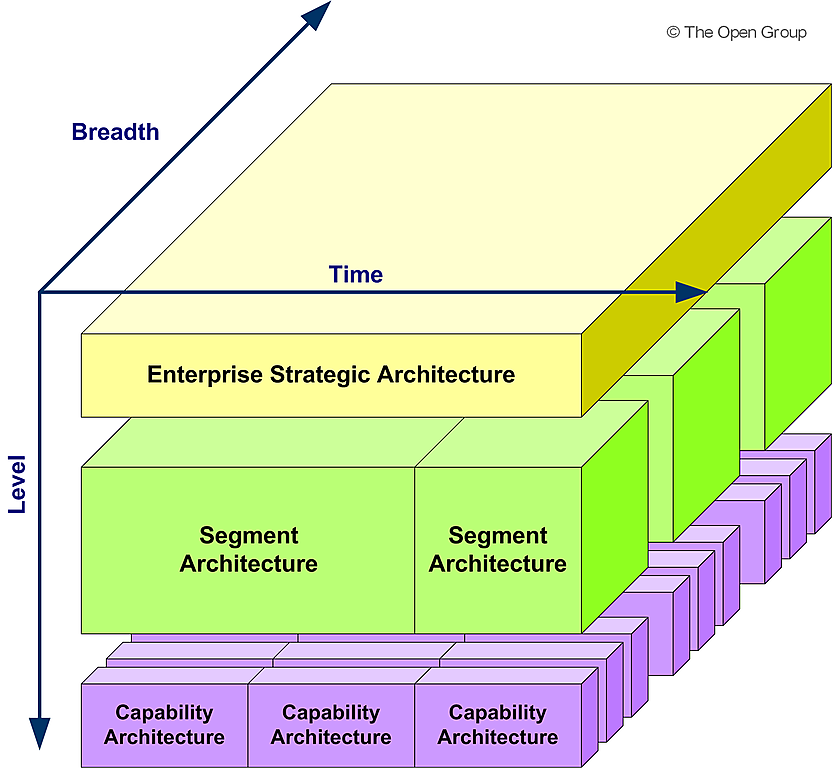
Architecture Landscape
The TOGAF standard uses the concepts of levels and the Enterprise Continuum to provide a framework for organizing the Architecture Landscape in a typical enterprise.
The Architecture Landscape can be quite complex, with many different architectures addressing different needs at different levels of detail. To address this complexity, the TOGAF standard defines three levels of granularity for organizing the Architecture Landscape:
- Strategic Architecture: This level provides an organizing framework for operational and change activity at an executive level. It is concerned with defining the overall direction and goals of the enterprise, and ensuring that the enterprise’s architecture is aligned with these goals.
- Segment Architecture: This level provides an organizing framework for operational and change activity at a program or portfolio level. It is concerned with defining the architecture for a specific part of the enterprise, such as a business unit or department. Segment Architecture enables the development of effective architecture roadmaps that align with the overall direction set by the Strategic Architecture.
- Capability Architecture: This level provides an organizing framework for change activity and the development of effective architecture roadmaps that realize capability increments. It is concerned with defining the specific capabilities that are required to support the business goals and objectives of the enterprise. Capability Architecture enables the development of incremental changes to the enterprise architecture, while ensuring that these changes are aligned with the overall direction set by the Strategic Architecture.
The Enterprise Continuum provides a further framework for organizing the Architecture Landscape, by defining a series of architecture development levels that correspond to the different stages of architecture development and maturity within the enterprise. This helps to ensure that the enterprise’s architecture is developed and managed in a consistent and coherent way, with a clear understanding of the relationships between different architecture components at different levels of granularity.
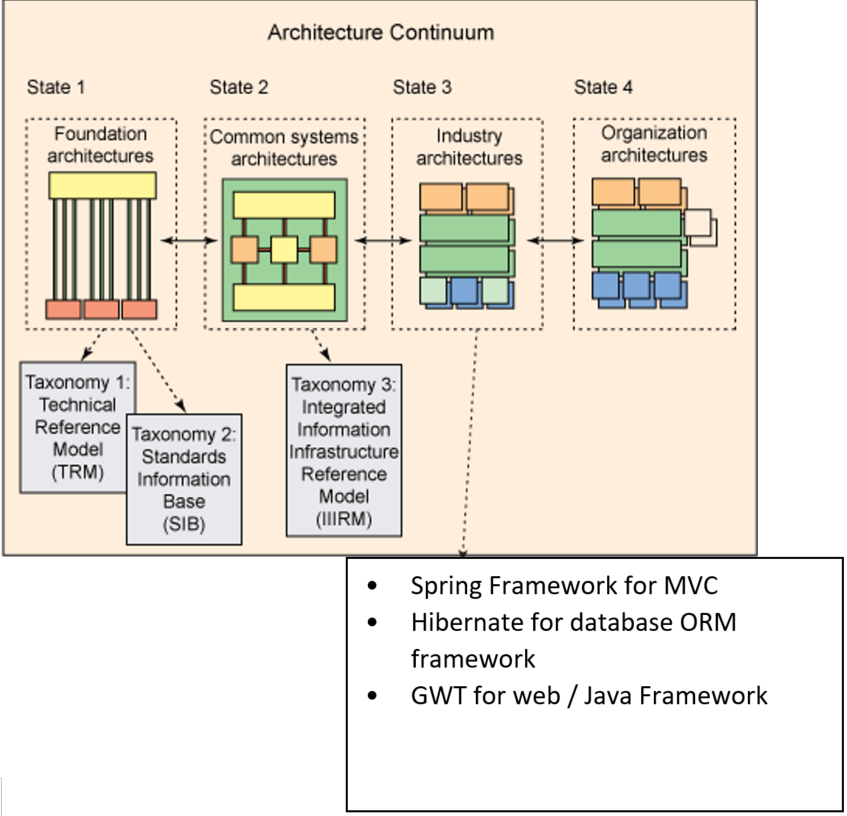
Standards Information Base (SIB) and Reference Library
the Architecture Repository is a key component of the framework, and it serves as a central storehouse for all architectural artifacts, templates, and other resources used by the organization to support its architecture development process. The Architecture Repository includes several components, two of which are:
- Standards Information Base (SIB): This component captures the standards and guidelines that new architectures must comply with. These standards may include industry standards, supplier products and services, or shared services that are already deployed within the organization. The SIB helps to ensure that new architectures are aligned with the organization’s strategic goals, objectives, and policies.
- Reference Library: This component provides a range of guidelines, templates, patterns, and other forms of reference material that can be leveraged in order to accelerate the creation of new architectures for the enterprise. The reference library can include architectural principles, best practices, and guidance on specific domains or technologies. The reference library helps to promote consistency and reuse across the organization,
Governance Log
The Governance Log within the Architecture Repository serves as a record of governance activity across the enterprise. It captures key decisions made by the governance board or other relevant stakeholders, as well as any associated rationale or justifications for those decisions.
The Governance Log can be accessed by architects and other stakeholders throughout the architecture development process to ensure that decisions are made in alignment with the organization’s overall architecture vision and goals. It can also be used to track the status of governance-related tasks and initiatives, such as the development of new standards or policies.
Architecture Requirements Repository
The Architecture Requirements Repository is a component of the Architecture Repository in TOGAF. It provides a view of all authorized architecture requirements that have been agreed upon by the Architecture Board. These requirements are typically derived from the organization’s business goals and objectives, and serve as a guide for the development of the enterprise architecture.
The Architecture Requirements Repository captures the full range of architecture requirements, including business, data, application, and technology requirements. It also includes any relevant constraints, assumptions, or dependencies associated with these requirements.
The purpose of the Architecture Requirements Repository is to ensure that all architecture development efforts are aligned with the organization’s strategic goals and objectives, and that they meet the needs of key stakeholders. By providing a centralized repository of authorized requirements, it helps to minimize duplication of effort and ensures that all architecture development efforts are consistent and coherent.
The Architecture Requirements Repository is typically maintained by the enterprise architecture team, and is used throughout the architecture development process to guide the development of the enterprise architecture. It is also used to assess the impact of changes to the enterprise architecture, and to ensure that all architecture development efforts are consistent with the organization’s overall architecture vision and goals.
Solutions Landscape
The Solutions Landscape is a component of the Architecture Repository in TOGAF. It presents an architectural representation of the Solution Building Blocks (SBBs) that support the Architecture Landscape and have been planned or deployed by the enterprise.
A Solution Building Block is a modular component of the architecture that represents a specific functional or technical capability. These SBBs can be combined to create more complex solutions that support the enterprise’s business objectives.
The Solutions Landscape provides an overview of the SBBs that have been planned or deployed by the enterprise. This includes both internal and external solutions, as well as any associated dependencies, interfaces, or interactions between these solutions.
The Solutions Landscape is typically used by architects and other stakeholders to identify opportunities for reuse and standardization, and to assess the impact of new solutions on the enterprise architecture. By providing a comprehensive view of the SBBs that support the Architecture Landscape, it helps to ensure that all solutions are developed in alignment with the organization’s overall architecture vision and goals.
Overall, the Solutions Landscape is an important tool for managing the complexity of the enterprise architecture, and for ensuring that all solutions are developed in a consistent and coherent manner. It helps to promote reuse, reduce duplication of effort, and support the ongoing evolution and maintenance of the enterprise architecture.














