The Use Case Scenario Analyzer is a powerful tool designed to transform a user-provided use case description into comprehensive decision tables with automated scenario analysis. This app provides a clear understanding of available scenarios and their consequences, serving as a foundation for detailed analysis, discussion, and test case creation to validate development work.
Step-by-Step Guide
Step 1: Access the Use Case Scenario Analyzer
-
Navigate to Tools in the main menu.
-
Select Apps from the dropdown.
-
Choose Use Case Scenario Analyzer.
-
Click Start Now to open the tool.
Step 2: Provide the Use Case Description
In the Use Case Scenario Analyzer interface, you will find a large text area for entering the use case description, which serves as the primary input for the app.
-
Enter the Description: Provide a detailed use case description, ideally including preconditions, main flow, alternative flows, and postconditions for optimal results.
-
Formatting: The tool supports markdown formatting, which is recommended for better readability and structure.
-
Input Options:
-
Direct Entry: Type the use case description directly into the text area.
-
Paste Content: Copy and paste a previously prepared use case description into the text area.
-
Use Case Description Generator: If you have used the Use Case Description Generator app, you can reuse the high-quality use case description generated by that tool.
-
-
Preview: A real-time preview is available to review the formatted input text.
-
Once satisfied with the use case description, click Identify Use Case Scenarios & Core Test Cases to proceed.
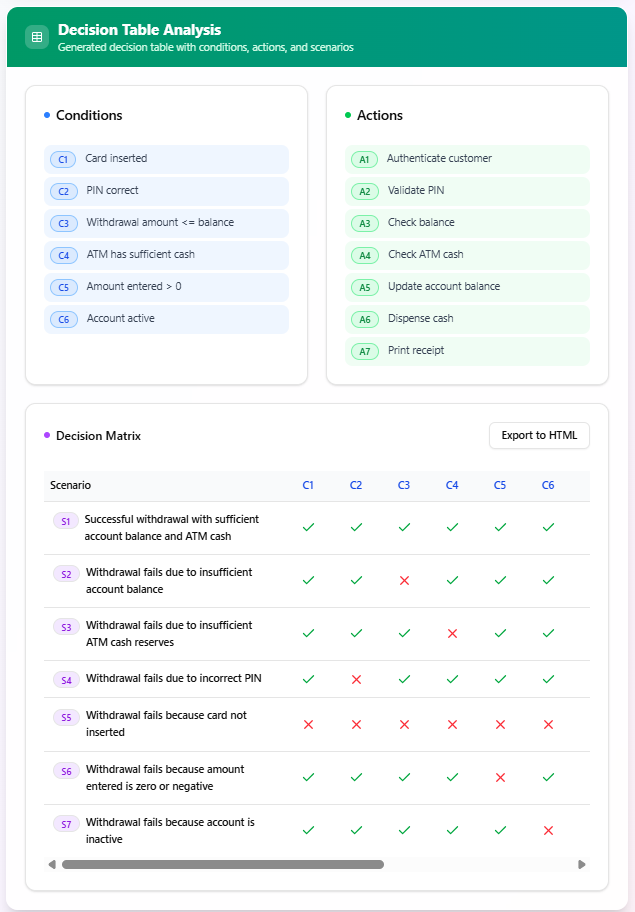
Step 3: Review Decision Table Analysis
The AI analyzes the provided use case description and generates three key outputs, presented as tables:
i. Conditions
A table listing the preconditions required to accomplish the use case. These conditions may be explicitly stated in the description or logically inferred by the AI. For example, for a “Withdraw Cash” use case in an ATM system, the conditions might include:
-
Card Inserted
-
PIN Correct
-
Withdrawal amount <= balance
- ATM has sufficient cash
- Amount entered > 0
-
Account active
ii. Actions
A table listing the actions that can occur as part of the use case. For the “Withdraw Cash” example, actions might include:
-
Authenticate customer
-
Validate PIN
-
Check balance
-
Check ATM cash
- Update account balance
-
Dispense cash
-
Print receipt
iii. Decision Matrix
The most comprehensive output, this table identifies all possible scenarios for the use case. Each row represents a unique scenario, and the columns are divided into two groups:
-
Conditions: The preconditions listed in the “Conditions” table, marked with a check mark (✓) for relevant conditions or a cross (✗) for irrelevant ones in each scenario.
-
Actions: The actions listed in the “Actions” table, marked with a check mark (✓) for actions executed in each scenario.
Example scenarios for the “Withdraw Cash” use case might include:
-
S1: Successful withdrawal with sufficient account balance and ATM cash
-
S2: Withdrawal fails due to insufficient account balance
-
S3: Withdrawal fails due to insufficient ATM cash reserves
-
S4: Withdrawal fails due to incorrect PIN
-
S5: Withdrawal fails because card not inserted
-
S6: Withdrawal fails because amount entered is zero or negative
-
S7: Withdrawal fails because account is inactive
The decision matrix provides a clear, structured overview of how conditions lead to specific actions in each scenario, enabling users to understand the use case comprehensively.
Step 4: Utilize the Decision Tables
The generated decision tables serve as a foundation for:
-
Detailed Analysis: Understand the relationships between conditions and actions in each scenario.
-
Discussion: Facilitate discussions with stakeholders to refine the use case or identify edge cases.
-
Test Case Development: Use the scenarios to create detailed test cases for validating development work.
If needed, revisit the use case description to refine the input and regenerate the decision tables for improved accuracy.
Key Notes
-
Automated Scenario Analysis: The AI leverages natural language processing to extract and analyze conditions, actions, and scenarios, streamlining the process of use case analysis.
-
Iterative Process: Users can edit the use case description and regenerate the decision tables to refine the output as needed.
-
Markdown Support: Using markdown formatting in the use case description enhances readability and ensures the AI accurately interprets the input.
Conclusion
By following these steps, you can effectively use the Use Case Scenario Analyzer to generate detailed decision tables that provide a clear picture of your use case’s scenarios and their consequences. This tool empowers users to perform in-depth analysis, facilitate discussions, and develop robust test cases to validate development work.














