Transforming Unstructured Problem Descriptions into Structured Domain Classes, Attributes, and Relationships Before Drawing Begins
After establishing a high-level system context through natural language prompts, the next critical step is to dive deeper into the domain itself. Most real-world requirements arrive as unstructured text: lengthy problem statements, user stories scattered across documents, email threads, meeting transcripts, product briefs, or even legacy specifications. Manually reading through this material to extract classes, attributes, operations, and relationships is time-consuming, error-prone, and highly subjective—different analysts often produce different initial models from the same text.
Visual Paradigm’s AI-Powered Textual Analysis tool changes this fundamentally. It acts as an intelligent first-pass analyzer that automates the heavy lifting of domain mining, delivering a structured, visual starting point—a UML Class Diagram—while leaving full editorial control in your hands. This feature bridges the gap between raw text and object-oriented design faster and more consistently than traditional manual approaches.
How AI-Powered Textual Analysis Works
The process is guided, iterative, and highly transparent, typically following these steps (accessible via the Innovation Hub’s “Textual Analysis” app or similar step-based tools in Visual Paradigm Online/Desktop):
- Provide or Generate the Problem Description
- Paste your existing requirements text, user stories, or project brief directly into the tool.
- Alternatively, start with a short app name or concept (e.g., “Online Library Management System”) and click Generate Problem Description.
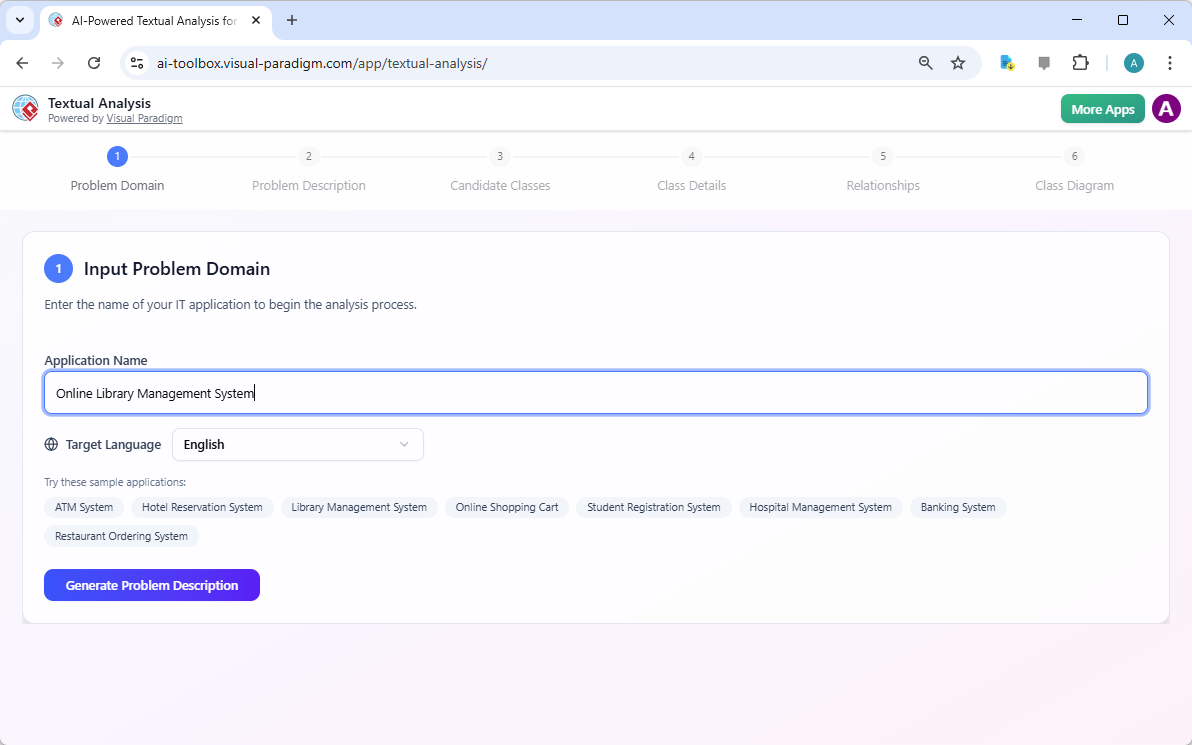
A screenshot of Visual Paradigm’s AI Powered Textual Analysis, which starts by submitting the name of the system The AI produces a coherent, paragraph-length summary you can edit for accuracy before proceeding. This ensures the input is focused and complete.
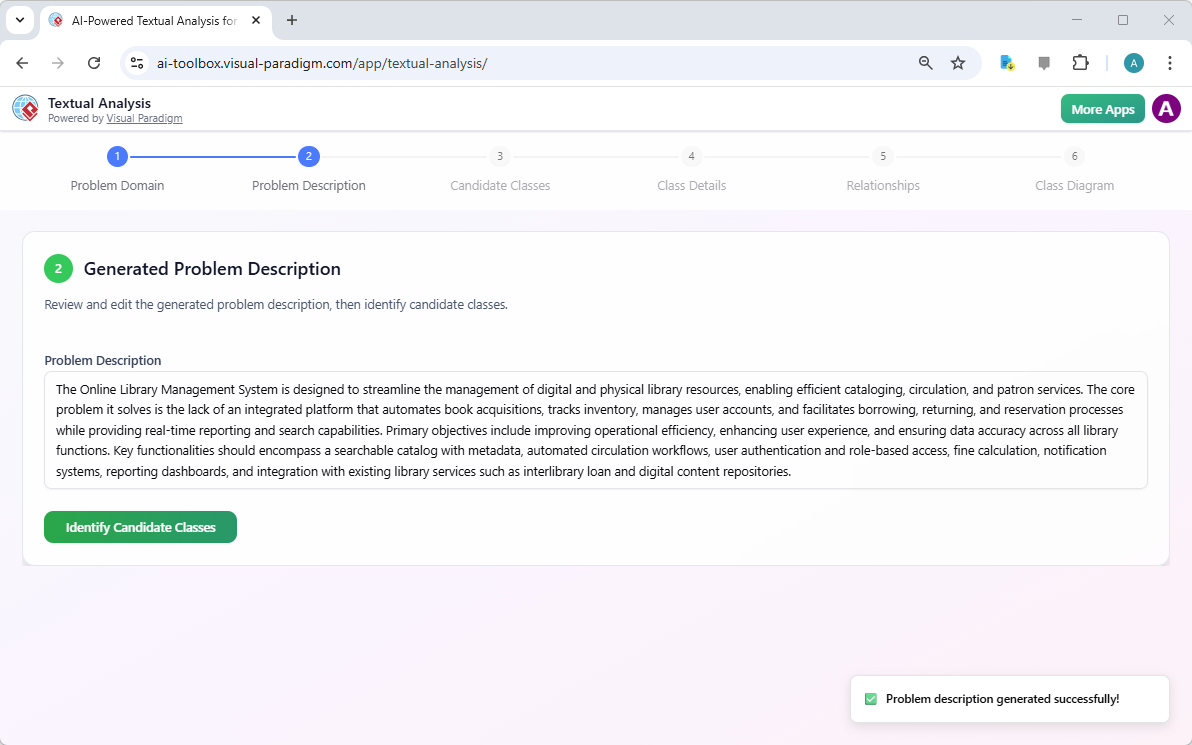
A problem description is generated by AI based on a concise problem domain description
- Identify Candidate Classes
- Click Identify Candidate Classes.
- The AI scans the text using natural language understanding tuned for software domain modeling. It highlights and lists potential domain entities (candidate classes) such as “Book,” “Patron,” “Loan,” “Librarian,” etc.
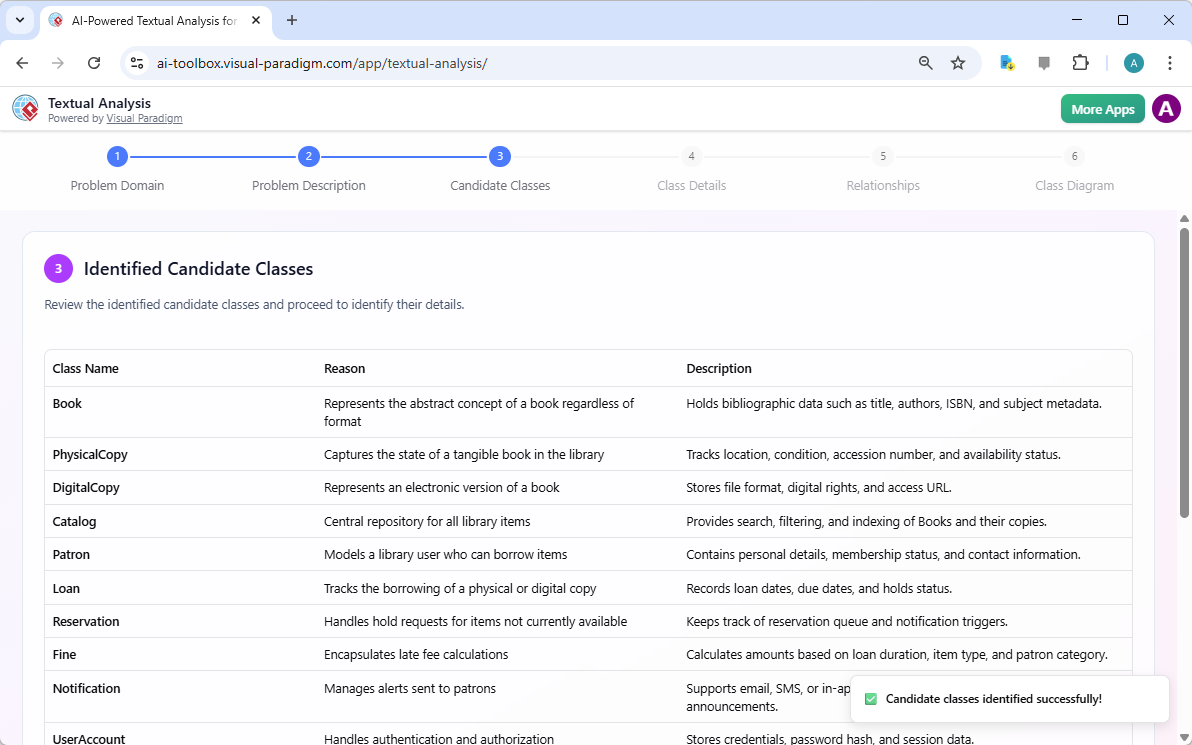
A list of candidate classes generated by AI, based on the problem description - Each suggestion includes:
- The identified noun or noun phrase from the text
- Reason or rationale
- Description
- The bottom part of the screen lists the nouns that are not qualified as candidate classes with the reasons why.
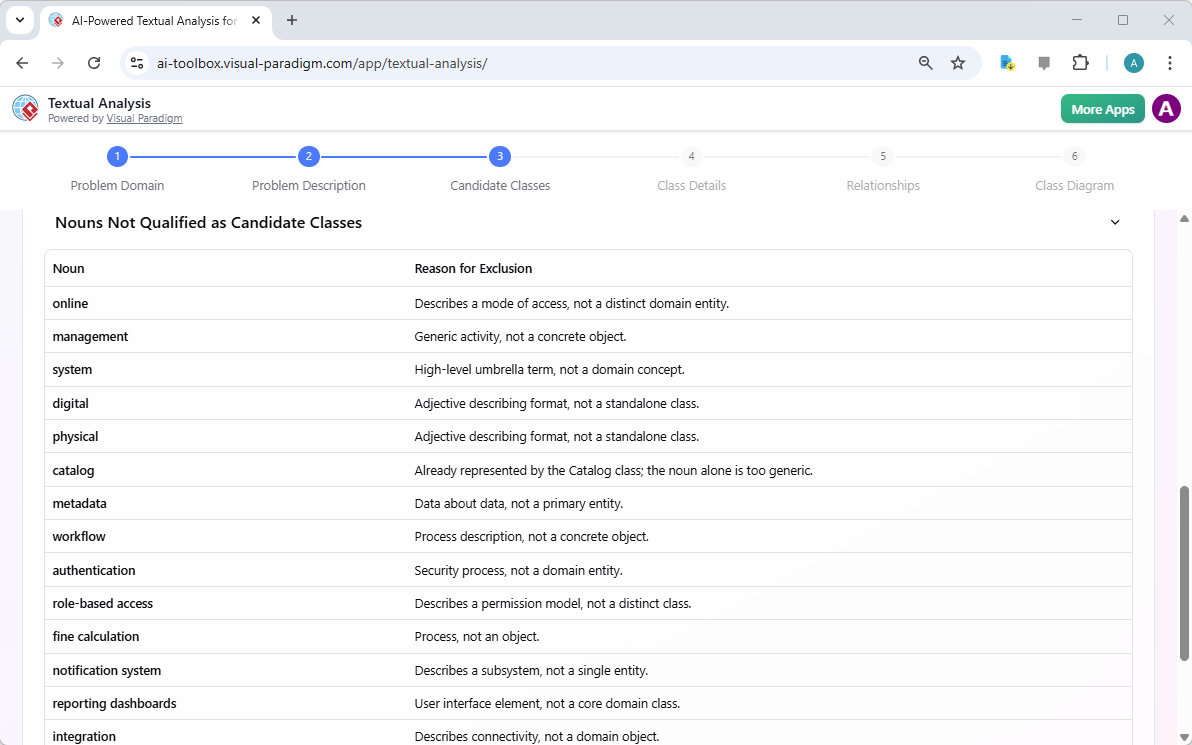
A list of candidate classes fouled
- Discover Attributes, Operations, and Relationships
- Click on Identify Details to proceed to the next guided step (e.g., Discover Attributes & Operations or Identify Relationships).
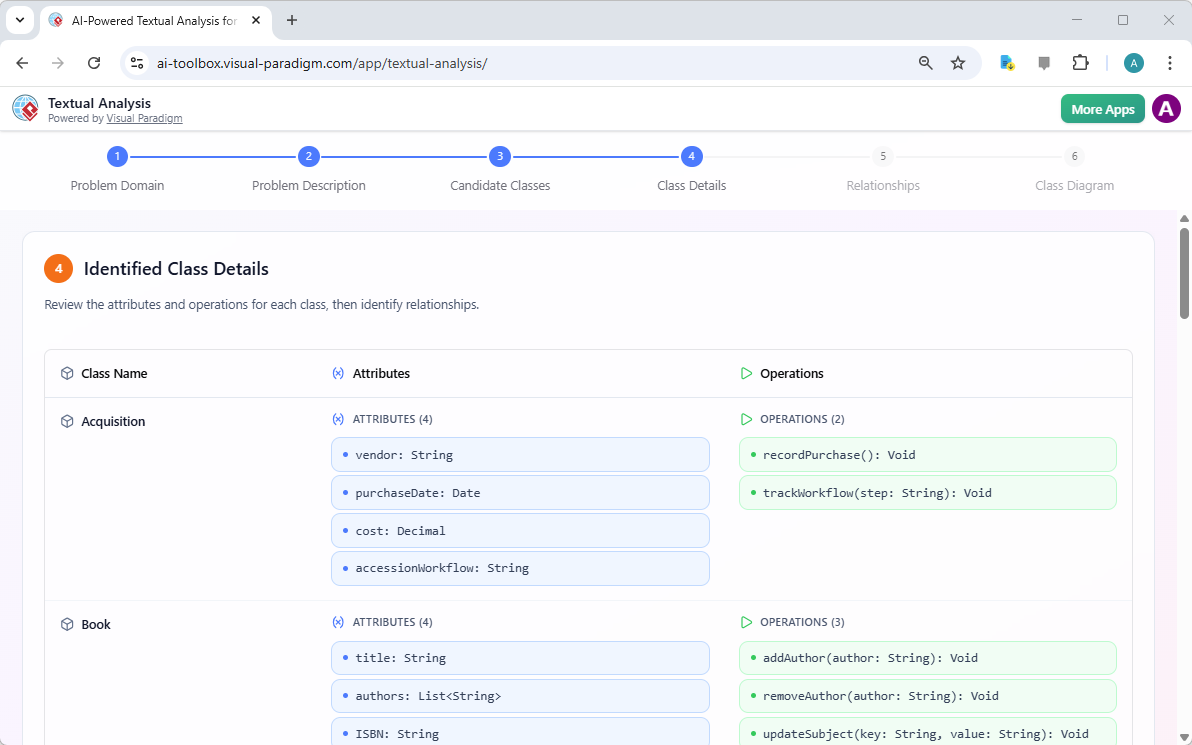
Class details populated, which includes the attributes and operations - The AI proposes:
- Attributes (e.g., Book → title: String, ISBN: String, publicationYear: int)
- Operations (methods/behaviors, e.g., Member → borrowBook(), returnBook())
- Relationships (associations, aggregations, compositions, generalizations, multiplicities) based on linguistic patterns (e.g., “owns,” “contains,” “is a,” “has many”)
- Suggestions appear in a clear, reviewable format—often with highlighted references back to the original text for traceability.
- Click on Identify Details to proceed to the next guided step (e.g., Discover Attributes & Operations or Identify Relationships).
- Identify Relationships
- Click on Identify Class Relationships to proceed to identifying the relationships among the classes.
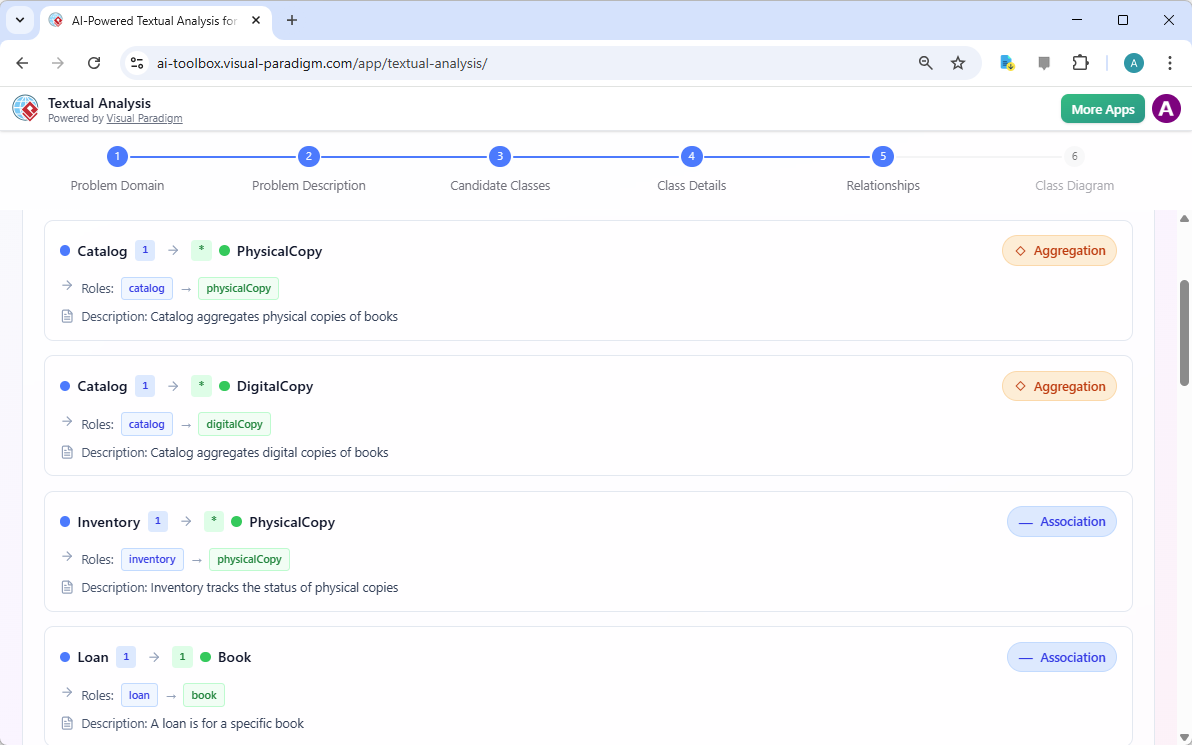
Relationships of the classes identified - The AI proposes:
- Relationships (associations, aggregations, compositions, generalizations, multiplicities) based on linguistic patterns (e.g., “owns,” “contains,” “is a,” “has many”)
- Click on Identify Class Relationships to proceed to identifying the relationships among the classes.
- Generate the Class Diagram
- Once satisfied with the candidates, click Generate Diagram.
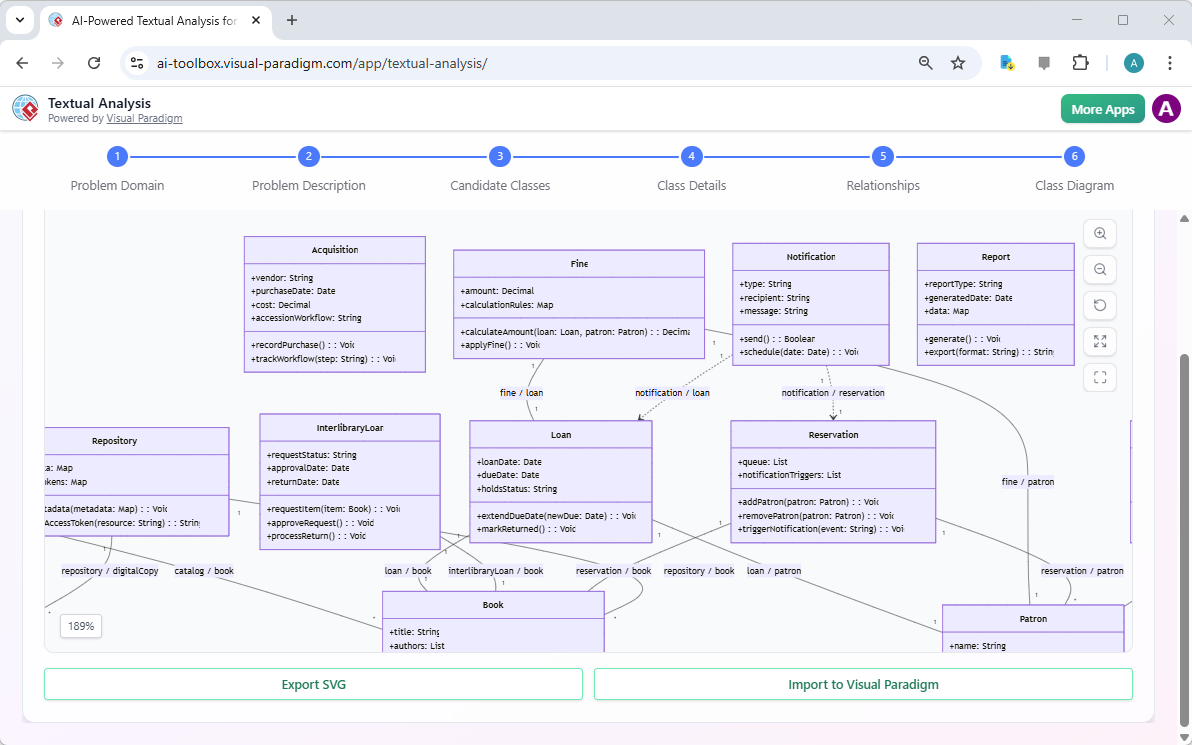
A class diagram is generated based originally on a given problem description - The tool instantly produces a complete, UML 2.5-compliant Class Diagram:
- Classes with compartments for attributes and operations
- Correctly notated relationships (lines with diamonds, arrows, multiplicities)
- Clean, professional layout (auto-arranged to minimize crossing lines and optimize readability)
- No manual drawing required—the diagram appears ready for immediate review.
- Once satisfied with the candidates, click Generate Diagram.
- Refine and Own the Model
- The generated diagram is fully editable. Click Import to Visual Paradigm (or import to desktop) to:
- Add missing elements
- Adjust visibility (+/-/#), data types, stereotypes, or constraints
- Apply design patterns
- Validate against OO principles
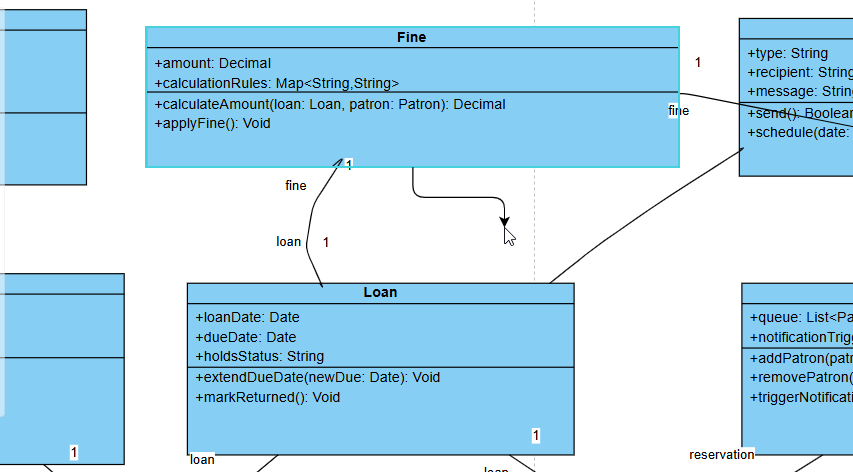
Editing a Class Diagram generated from AI Chatbot in Visual Paradigm’s online class diagram editor
- This ensures the AI provides an excellent 70–80% foundation, while your expertise handles nuances, business rules, and edge cases.
- The generated diagram is fully editable. Click Import to Visual Paradigm (or import to desktop) to:
Why This Approach Is Transformative
| Challenge in Traditional Domain Discovery | Benefit with AI-Powered Textual Analysis |
|---|---|
| Manual scanning of text is slow and misses items | AI extracts candidates comprehensively in seconds |
| Inconsistent results across team members | Objective, repeatable suggestions based on trained standards |
| Relationships often overlooked or incorrectly modeled | Automatically detects and proposes associations, multiplicities, etc. |
| Starting diagram delayed by extraction effort | Visual Class Diagram available before any manual drawing |
| Traceability to source text is lost | Suggestions link back to original phrases for easy verification |
| Beginners struggle with OO abstraction | Guided steps + educational hints teach while building |
Real-World Impact
- Accelerated Kickoff — Turn a 10-page requirements doc into a reviewable domain model in minutes instead of days.
- Better Stakeholder Alignment — Show a visual model early in discussions: “Here’s what the system entities look like based on your description—does this match your vision?”
- Reduced Rework — Catch terminology inconsistencies, missing concepts, or flawed relationships before investing in use cases or sequences.
- Educational Value — Teams learn domain modeling patterns implicitly through AI suggestions and step-by-step rationale.
This section equips you to take any textual artifact—however messy—and emerge with a solid, structured domain foundation. The resulting Class Diagram becomes the anchor for all subsequent modeling: use case elaboration, behavioral dynamics, architectural layering, and beyond.
In the next part of Module 2, we’ll explore guided wizards that build on this extracted model for even more systematic refinement and completeness. The era of staring at blank canvases while drowning in text is over—AI now does the mining so you can do the mastering.